The Role of CD40 in Allergic Rhinitis and Airway Remodelling
- PMID: 33976586
- PMCID: PMC8087476
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6694109
The Role of CD40 in Allergic Rhinitis and Airway Remodelling
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) affects millions of people and is lack of effective treatment. CD40 is an important costimulatory molecule in immunity. However, few studies have focused on the role of CD40 in AR.
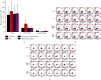
Methods: In this study, we built mouse model of chronic AR. The mice were divided into the AR, control, intravenous CD40 siRNA, and nasal CD40 siRNA groups (n = 6 each). We detected OVA-sIgE, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-10, IFN-γ, and TGF-β levels in serum and supernatant by ELISA, CD40+ splenic DCs, and Foxp3+ Tregs by flow cytometry and CD40 mRNA by RT2-PCR. We also used PAS and MT stains to assess tissue remodelling.
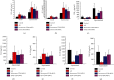
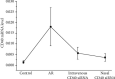
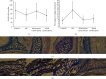
Results: (1) The OVA-sIgE, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 levels in the serum or supernatant of nasal septal membrane of AR mice were significantly higher than control. After treated with CD40 siRNA, those indicators were significantly decreased. The IFN-γ, IL-10, and TGF-β levels in AR mice were significantly lower than that in control and were increased by administration of CD40 siRNA. (2) AR mice had significantly fewer Foxp3+ Tregs in the spleen than control mice. After treated with CD40 siRNA, AR mice had significantly more Foxp3+ Tregs. (3) AR mice exhibited a significantly higher CD40 mRNA levels than control. Administration of CD40 siRNA significantly reduced the CD40 mRNA level. (4) The AR mice showed significantly greater collagen deposition than the control in MT staining. Applications of CD40 siRNA significantly reduced the collagen deposition in AR mice.
Conclusion: CD40 siRNA therapy shows promise for chronic AR as it significantly attenuated allergic symptoms and Th2-related inflammation and upregulated Foxp3+ Tregs. CD40 plays a role in tissue remodelling in AR, which can be inhibited by CD40 siRNA application.
Copyright © 2021 Ke-Jia Cheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Derp1-modified dendritic cells attenuate allergic inflammation by regulating the development of T helper type1(Th1)/Th2 cells and regulatory T cells in a murine model of allergic rhinitis.Mol Immunol. 2017 Oct;90:172-181. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2017.07.015. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28802126
-
Changes in respiratory tract and gut microbiota in AR mice and their relationship with Th1/Th2/Treg.Microb Pathog. 2024 Oct;195:106881. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106881. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39197690
-
A novel allergen-specific therapy with regulatory T cells induced by CD40-silenced dendritic cells.Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2019 Dec;37(4):240-248. doi: 10.12932/AP-240418-0302. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30525745
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Ameliorates Allergic Rhinitis by Reversing the Imbalance of Th1/Th2 and Up-Regulation of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Regulatory T Cells, Interleukin-10, and Membrane-Bound Transforming Growth Factor-β in Guinea Pigs.Inflammation. 2018 Feb;41(1):81-92. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0666-6. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 28894978
-
Nonylphenol can aggravate allergic rhinitis in a murine model by regulating important Th cell subtypes and their associated cytokines.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 May;70:260-267. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.02.030. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30851706
Cited by
-
Blocking CD40 Alleviates Th1 and Th17 Cell Responses in Elastin Peptide-Induced Murine Emphysema.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023 Nov 23;18:2687-2698. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S428832. eCollection 2023. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2023. PMID: 38022831 Free PMC article.
-
IL-4/IL-13 Axis in Allergic Rhinitis: Elevated Serum Cytokines Levels and Inverse Association With Tight Junction Molecules Expression.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Mar 17;9:819772. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.819772. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35372516 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of inhalation of essential oils from Mentha piperita leaf on tight junctions and inflammation in allergic rhinitis.Front Allergy. 2022 Dec 12;3:1012183. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.1012183. eCollection 2022. Front Allergy. 2022. PMID: 36578435 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

