Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Caused by Erlotinib in a Patient with Lung Cancer
- PMID: 33976640
- PMCID: PMC8077539
- DOI: 10.1159/000514146
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis Caused by Erlotinib in a Patient with Lung Cancer
Abstract
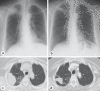
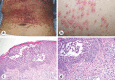
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP) is a rare drug-related adverse skin reaction caused mainly by antibiotics. Erlotinib is an epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) used to treat lung cancer. A 69-year-old woman with primary lung cancer (adenocarcinoma, cT3N1M1b, stage IVB) developed erythema and multiple skin pustules on her abdomen and both thighs after 7 weeks of erlotinib treatment. She also had fever and general fatigue. Histological examination of a skin biopsy specimen showed intraepidermal pustules with neutrophil and eosinophil infiltration. She was diagnosed with erlotinib-induced AGEP. AGEP resolved by erlotinib discontinuation and systemic corticosteroid treatment. The lung cancer progressed when erlotinib was discontinued, so afatinib, a second-generation EGFR-TKI, was administrated without any skin adverse effects. Afatinib successfully decreased the lung cancer, and maintained the disease stable for 1 year. Although acneiform rash was the most common skin adverse event caused by EGFR, AGEP rarely occurred. The present case also demonstrated that it is possible to switch agents, from erlotinib to afatinib, even though they have the same pharmacological effects. Although AGEP is a rare drug-related skin disorder, physicians should be aware that erlotinib may induce AGEP.
Keywords: Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis; Erlotinib; Lung cancer; Skin disorder.
Copyright © 2021 by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Roujeau JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Bourseau C, Guillaume JC, Bernard P, Lok C, et al. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. Analysis of 63 cases. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127((9)):1333–8. - PubMed
-
- Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Vaillant L, Roujeau JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)–a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001;28((3)):113–9. - PubMed
-
- Szatkowski J, Schwartz RA. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP): A review and update. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;73((5)):843–8. - PubMed
-
- Sidoroff A, Dunant A, Viboud C, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Naldi L, et al. Risk factors for acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)-results of a multinational case-control study (EuroSCAR) Br J Dermatol. 2007;157((5)):989–96. - PubMed
-
- Greenhalgh J, Dwan K, Boland A, Bates V, Vecchio F, Dundar Y, et al. First-line treatment of advanced epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation positive non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;((5)):CD010383. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

