Opposing and Operated Side Electroacupuncture Generates Similar Analgesic Effects on Pain after Knee Surgery
- PMID: 33976704
- PMCID: PMC8087472
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6616886
Opposing and Operated Side Electroacupuncture Generates Similar Analgesic Effects on Pain after Knee Surgery
Abstract
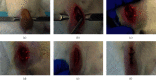
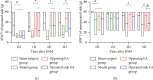
The purpose of this study was to investigate whether opposing electroacupuncture (EA) could produce similar analgesic effects as operated side EA after knee surgery in rats. Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into the sham surgery group, and three surgery groups: opposing EA, operated side EA, and model. After surgery, compared with the sham surgery group, three kinds of pain behavior test methods (mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT), cumulative pain score [CPS], and mechanical hypersensitivity of knee) were used to assess the pain behavior of the rats in the surgery groups. After knee surgery, the three surgery groups were intervened for three consecutive days: EA on the nonoperated side in the opposing EA group, EA on the operated side in the operated side EA group, and no intervention in the model group. It was shown that MWT was higher and CPS was lower in the two EA groups than in the model group on the first and second days after surgery. On the third day after surgery, MWT in the two EA groups was the highest among the 3 days, CPS was the lowest among the 3 days, and the number of nonvocalizations in rats also increased compared with the model group. Moreover, the MWT of the nonoperated side increased more in the opposing EA group than in the model and operated side EA groups. This indicated that both opposing EA and operated side EA methods can be used to relieve pain after knee joint surgery.
Copyright © 2021 Hai Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest and no financial interests regarding the publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Effects of electroacupuncture on activation of microglia cells in spinal cord in rats with neuropathic pain].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2017 Apr 12;37(4):411-416. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.2017.04.016. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2017. PMID: 29231595 Chinese.
-
Analgesic Effects and Neuropathology Changes of Electroacupuncture on Curing a Rat Model of Brachial Plexus Neuralgia Induced by Cobra Venom.Pain Physician. 2016 Mar;19(3):E435-47. Pain Physician. 2016. PMID: 27008299
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture on angiopoietin-1 in spinal cord of rats with neuropathic pain].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Mar 25;46(3):209-14. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.200269. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 33798293 Chinese.
-
[Effect of electroacupuncture on pain threshold and spinal NR2B subunit expression in a rat model of neuropathic pain].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010 Dec;30(12):2702-4. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 21177185 Chinese.
-
[Effects of electroacupuncture on glutamate and aspartic acid contents in the dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord in rats with neuropathic pain].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2008 Aug;33(4):250-4. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2008. PMID: 18928117 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effects of Electroacupuncture on Gastrointestinal Motility Function, Pain, and Inflammation via Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 in a Rat Model after Colonic Anastomoses.Dis Markers. 2022 Jul 5;2022:5113473. doi: 10.1155/2022/5113473. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35845135 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

