Hsa_circ_0091581 promotes glioma progression by regulating RMI1 via sponging miR-1243-5p
- PMID: 33976734
- PMCID: PMC8100801
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.55558
Hsa_circ_0091581 promotes glioma progression by regulating RMI1 via sponging miR-1243-5p
Abstract
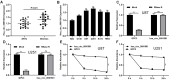
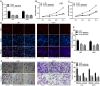
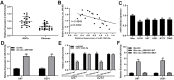
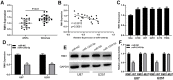
Glioma is a pervasive malignancy and the main cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Circular RNA is an important subject of cancer research, and its role and function in glioma are poorly understood. This study demonstrated that hsa_circ_0091581 is upregulated in glioma tissues and cells. The results of the CCK-8, EdU, and transwell assays indicated that hsa_circ_0091581 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells. The results of the luciferase reporter and RNA immunoprecipitation assays indicated that the mechanism of the effects of hsa_circ_0091581 on glioma cells involves sponging miR-1243-5p to regulate RMI1. The results of the rescue experiments indicated that hsa_circ_0091581 regulates proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells by targeting RMI1 in a miR-1243-5p dependent manner. The results of the nude mice xenograft assays showed that knockdown of hsa_circ_0091581 inhibits glioma growth in vivo. Thus, our study determined the role of hsa_circ_0091581/miR-1243-5p/RMI1 in glioma and suggests that this axis may be a novel therapeutic target in glioma.
Keywords: circ_0091581; miR-1243-5p, RMI1, glioma..
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang X, Wang S, Lin G, Wang D. Down-regulation of circ-PTN suppresses cell proliferation, invasion and glycolysis in glioma by regulating miR-432-5p/RAB10 axis. Neurosci Lett. 2020;735:135153. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

