The Yunnan national medicine Maytenus compound inhibits the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by suppressing the activation of the EGFR-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway
- PMID: 33976742
- PMCID: PMC8100817
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.56426
The Yunnan national medicine Maytenus compound inhibits the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by suppressing the activation of the EGFR-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway
Abstract
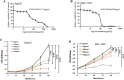
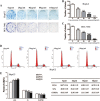
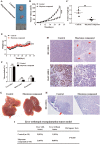
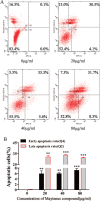
Objective: To investigate the effects of Maytenus compound on the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells in vitro and in vivo and to explore the underlying mechanism. Methods: The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of Maytenus compound in HepG2 and BEL-7402 cells were determined by the MTS assay. HepG2 and BEL-7402 cells were treated with different concentrations of Maytenus compound. MTS assays, colony formation assays and cell cycle analyses were performed to clarify the inhibitory effect of Maytenus compound on the proliferation of HepG2 and BEL-7402 cells in vitro. After subcutaneous injection of HepG2 cells, nude mice were randomly divided into a vehicle control group and a drug intervention group, which were intragastrically administered ddH2O or Maytenus compound, respectively. The inhibitory effect of Maytenus compound on the proliferation of HepG2 cells in vivo was analyzed using subcutaneous tumor growth curves, tumor weight, the tumor growth inhibition rate and the immunohistochemical detection of BrdU-labeled cells in S phase. The organ toxicity of Maytenus compound was initially evaluated by comparing the weight difference and organ index of the two groups of nude mice. The main proteins in the EGFR-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway were detected by Western blot after Maytenus compound intervention in vivo and in vitro. Results: Maytenus compound showed favorable antiproliferation activity against HepG2 and BEL-7402 cells with IC50 values of 79.42±11.71 µg/mL and 78.48±8.87 µg/mL, respectively. MTS assays, colony formation assays and cell cycle analyses showed that Maytenus compound at different concentration gradients within the IC50 concentration range significantly suppressed the proliferation of HepG2 and BEL-7402 cells in vitro and inhibited cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase. Additionally, Maytenus compound, at an oral dose of 2.45 g/kg, dramatically inhibited, without obvious organ toxicity, the proliferation of subcutaneous tumors formed by HepG2 cells in nude mice. In addition, the tumor growth inhibition rate for Maytenus compound was 66.94%. Furthermore, Maytenus compound inhibited the proliferation of liver orthotopic transplantation tumors in nude mice. Western blot analysis showed that Maytenus compound significantly downregulated the expression of p-EGFR, p-PI3K, and p-AKT and upregulated the expression of p-FOXO3a, p27, and p21 in vivo and in vitro. Conclusion: Maytenus compound significantly inhibited the proliferation of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo. The downregulation of the EGFR-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway and subsequent inhibition of cell cycle progression from G1 to S phase is one of the possible mechanisms. Maytenus compound has a high tumor growth inhibition rate and has no obvious organ toxicity, which may make it a potential anti-HCC drug, but the results from this study need to be confirmed by further clinical trials in HCC patients.
Keywords: EGFR-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway; Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC); Maytenus compound; Proliferation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Luo P, Wu S, Yu Y, Ming X, Li S, Zuo X. et al. Current Status and Perspective Biomarkers in AFP Negative HCC: Towards Screening for and Diagnosing Hepatocellular Carcinoma at an Earlier Stage. Pathology oncology research: POR. 2020;26:599–603. - PubMed
-
- Ang C, O'Reilly EM, Abou-Alfa GK. Targeted agents and systemic therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent results in cancer research Fortschritte der Krebsforschung Progres dans les recherches sur le cancer. 2013;190:225–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

