Bipedal locomotion in Octopus vulgaris: A complementary observation and some preliminary considerations
- PMID: 33976767
- PMCID: PMC8093653
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.7328
Bipedal locomotion in Octopus vulgaris: A complementary observation and some preliminary considerations
Abstract
Lacking an external shell and a rigid endoskeleton, octopuses exhibit a remarkable flexibility in their movements. Bipedal locomotion is perhaps the most iconic example in this regard. Until recently, this peculiar mode of locomotion had been observed only in two species of tropical octopuses: Amphioctopus marginatus and Abdopus aculeatus. Yet, recent evidence indicates that bipedal walking is also part of the behavioral repertoire of the common octopus, Octopus vulgaris. Here we report a further observation of a defense behavior that encompasses both postural and locomotory elements of bipedal locomotion in this cephalopod. By highlighting differences and similarities with the other recently published report, we provide preliminary considerations with regard to bipedal locomotion in the common octopus.
Keywords: Octopus; behavioral flexibility; bipedal; cephalopods; locomotion; walking.
© 2021 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
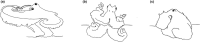
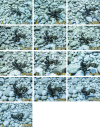
References
-
- Amodio, P. , Shigeno, S. , & Ostojić, L. (2020). Evolution of intelligence in cephalopods. eLS, 1, 77–84. 10.1002/9780470015902.a0029004 - DOI
-
- Amor, M. , Doyle, S. , Norman, M. , Roura, A. , Hall, N. , Robinson, A. , Leite, T. , & Strugnell, J. (2019). Genome‐wide sequencing uncovers cryptic diversity and mito‐nuclear discordance in the octopus vulgaris species complex. bioRxiv, 573493. 10.1101/573493 - DOI
-
- Borrelli, L. , Gherardi, F. , & Fiorito, G. (2006). A catalogue of body patterning in cephalopoda. Firenze University Press.
-
- Chellapurath, M. , Stefanni, S. , Fiorito, G. , Sabatini, A. M. , Laschi, C. , & Calisti, M. (2020). Locomotory behaviour of the intertidal marble crab (Pachygrapsus marmoratus) supports the underwater spring‐loaded inverted pendulum as a fundamental model for punting in animals. Bioinspiration and Biomimetics, 15(5), 055004. 10.1088/1748-3190/ab968c - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Luca, D. , Catanese, G. , Procaccini, G. , & Fiorito, G. (2014). An integration of historical records and genetic data to the assessment of global distribution and population structure in Octopus vulgaris . Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 2, 55. 10.3389/fevo.2014.00055 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

