Using data mining techniques to fight and control epidemics: A scoping review
- PMID: 33977022
- PMCID: PMC8102070
- DOI: 10.1007/s12553-021-00553-7
Using data mining techniques to fight and control epidemics: A scoping review
Abstract
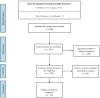
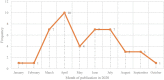
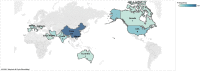
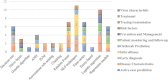
The main objective of this survey is to study the published articles to determine the most favorite data mining methods and gap of knowledge. Since the threat of pandemics has raised concerns for public health, data mining techniques were applied by researchers to reveal the hidden knowledge. Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed databases were selected for systematic searches. Then, all of the retrieved articles were screened in the stepwise process according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses checklist to select appropriate articles. All of the results were analyzed and summarized based on some classifications. Out of 335 citations were retrieved, 50 articles were determined as eligible articles through a scoping review. The review results showed that the most favorite DM belonged to Natural language processing (22%) and the most commonly proposed approach was revealing disease characteristics (22%). Regarding diseases, the most addressed disease was COVID-19. The studies show a predominance of applying supervised learning techniques (90%). Concerning healthcare scopes, we found that infectious disease (36%) to be the most frequent, closely followed by epidemiology discipline. The most common software used in the studies was SPSS (22%) and R (20%). The results revealed that some valuable researches conducted by employing the capabilities of knowledge discovery methods to understand the unknown dimensions of diseases in pandemics. But most researches will need in terms of treatment and disease control.
Keywords: COVID-19; Data mining; Pandemics; Review.
© IUPESM and Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Data Quality- and Utility-Compliant Anonymization of Common Data Model-Harmonized Electronic Health Record Data: Protocol for a Scoping Review.JMIR Res Protoc. 2023 Aug 11;12:e46471. doi: 10.2196/46471. JMIR Res Protoc. 2023. PMID: 37566443 Free PMC article.
-
Visual Analytic Tools and Techniques in Population Health and Health Services Research: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Dec 3;22(12):e17892. doi: 10.2196/17892. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 33270029 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in the Fight Against COVID-19: Scoping Review.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Dec 15;22(12):e20756. doi: 10.2196/20756. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 33284779 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical methods for identifying sequences of utilization in health data: a scoping review.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023 Sep 27;23(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12874-023-02019-y. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023. PMID: 37759162 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Text mining in mosquito-borne disease: A systematic review.Acta Trop. 2022 Jul;231:106447. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2022.106447. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Acta Trop. 2022. PMID: 35430265 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the most influential factors affecting outcomes of lung transplant recipients: a multivariate prediction model based on UNOS Data.BMJ Open. 2025 May 16;15(5):e089796. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-089796. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40379311 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence and COVID-19: A Systematic umbrella review and roads ahead.J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci. 2022 Sep;34(8):5898-5920. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2021.07.010. Epub 2021 Jul 15. J King Saud Univ Comput Inf Sci. 2022. PMID: 37520766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Text and data mining in health research: reflections on copyright.Cad Saude Publica. 2024 May 20;40(5):e00169023. doi: 10.1590/0102-311XPT169023. eCollection 2024. Cad Saude Publica. 2024. PMID: 38775612 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R. Features, evaluation, and treatment coronavirus (COVID-19). StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
