Bio-Inspired Soft Grippers Based on Impactive Gripping
- PMID: 33977041
- PMCID: PMC8097330
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202002017
Bio-Inspired Soft Grippers Based on Impactive Gripping
Abstract
Grasping and manipulation are fundamental ways for many creatures to interact with their environments. Different morphologies and grasping methods of "grippers" are highly evolved to adapt to harsh survival conditions. For example, human hands and bird feet are composed of rigid frames and soft joints. Compared with human hands, some plants like Drosera do not have rigid frames, so they can bend at arbitrary points of the body to capture their prey. Furthermore, many muscular hydrostat animals and plant tendrils can implement more complex twisting motions in 3D space. Recently, inspired by the flexible grasping methods present in nature, increasingly more bio-inspired soft grippers have been fabricated with compliant and soft materials. Based on this, the present review focuses on the recent research progress of bio-inspired soft grippers based on impactive gripping. According to their types of movement and a classification model inspired by biological "grippers", soft grippers are classified into three types, namely, non-continuum bending-type grippers, continuum bending-type grippers, and continuum twisting-type grippers. An exhaustive and updated analysis of each type of gripper is provided. Moreover, this review offers an overview of the different stiffness-controllable strategies developed in recent years.
Keywords: bio‐inspired materials; smart materials; soft actuators; soft grippers; soft robotics; variable stiffness.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

















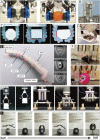
References
-
- Hughes J., Culha U., Giardina F., Guenther F., Rosendo A., Iida F., Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 69.
-
- Rus D., Tolley M. T., Nature 2015, 521, 467. - PubMed
-
- Pfeifer R., Lungarella M., Iida F., Commun. ACM 2012, 55, 76.
-
- Dickinson M. H., Farley C. T., Full R. J., Koehl M. A. R., Kram R., Lehman S., Science 2000, 288, 100. - PubMed
-
- Croll A. B., Hosseini N., Bartlett M. D., Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900193.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
