A Mutational Survey of Acral Nevi
- PMID: 33978681
- PMCID: PMC8117064
- DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0793
A Mutational Survey of Acral Nevi
Abstract
Importance: Acral skin may develop nevi, but their mutational status and association with acral melanoma is unclear.
Objective: To perform targeted next-generation sequencing on a cohort of acral nevi to determine their mutational spectrum.
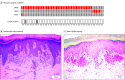
Design, setting, and participants: Acral nevi specimens (n = 50) that had been obtained for diagnostic purposes were identified from the pathology archives of a tertiary care academic cancer center and a university dermatology clinic. Next-generation sequencing was performed on DNA extracted from the specimens, and mutations called. A subset of samples was stained immunohistochemically for the BRAF V600E mutation.
Results: A total of 50 nevi from 49 patients (19 males and 30 females; median [range] age, 48 [13-85] years) were examined. Analysis of the sequencing data revealed a high prevalence of BRAF mutations (n = 43), with a lower frequency of NRAS mutations (n = 5). Mutations in BRAF and NRAS were mutually exclusive.
Conclusions and relevance: In this cohort study, nevi arising on mostly sun-protected acral skin showed a rate of BRAF mutation similar to that of acquired nevi on sun-exposed skin but far higher than that of acral melanoma. These findings are in contrast to the well-characterized mutational landscape of acral melanoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Two Trajectories to Melanoma on the Hands and Feet.JAMA Dermatol. 2021 Jul 1;157(7):769-770. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0792. JAMA Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33978680 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

