Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the pediatric bowel
- PMID: 33978797
- PMCID: PMC8113288
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-020-04868-x
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the pediatric bowel
Abstract
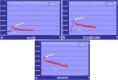
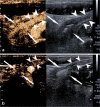
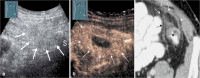
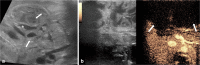
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) has emerged as a valuable modality for bowel imaging in adults and children. CEUS enables visualization of the perfusion of the bowel wall and of the associated mesentery in healthy and disease states. In addition, CEUS images can be used to make quantitative measurements of contrast kinetics, allowing for objective assessment of bowel wall enhancement. Bowel CEUS is commonly applied to evaluate inflammatory bowel disease and to monitor treatment response. It has also been applied to evaluate necrotizing enterocolitis, intussusception, appendicitis and epiploic appendagitis, although experience with these applications is more limited. In this review article, we present the current experience using CEUS to evaluate the pediatric bowel with emphasis on inflammatory bowel disease, extrapolating the established experience from adult studies. We also discuss emerging applications of CEUS as an adjunct or problem-solving tool for evaluating bowel perfusion.
Keywords: Bowel; Children; Contrast-enhanced ultrasound; Crohn disease; Inflammatory bowel disease; Ultrasound; Ultrasound contrast agents.
© 2021. Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Dillman receives grant funding from Bracco Diagnostics.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Contrast-enhanced US in Pediatric Patients: Overview of Bowel Applications.Radiographics. 2020 Oct;40(6):1743-1762. doi: 10.1148/rg.2020200019. Radiographics. 2020. PMID: 33001781 Review.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for musculoskeletal indications in children.Pediatr Radiol. 2021 Nov;51(12):2303-2323. doi: 10.1007/s00247-021-04964-6. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Pediatr Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33783575 Review.
-
Usefulness of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD).Dig Liver Dis. 2018 Aug;50(8):761-767. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2018.03.023. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Dig Liver Dis. 2018. PMID: 29705029 Review.
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy of the Neonatal Bowel: Novel, Bedside, Noninvasive, and Radiation-Free Imaging for Early Detection of Necrotizing Enterocolitis.Am J Perinatol. 2018 Dec;35(14):1358-1365. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1655768. Epub 2018 May 31. Am J Perinatol. 2018. PMID: 29852509 Review.
-
Quantitative analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography of the bowel wall can predict disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease.Eur J Radiol. 2014 Aug;83(8):1317-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.05.012. Epub 2014 May 16. Eur J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24908589
Cited by
-
Ultrasound for necrotizing enterocolitis: how can we optimize imaging and what are the most critical findings?Pediatr Radiol. 2023 Jun;53(7):1237-1247. doi: 10.1007/s00247-022-05545-x. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Pediatr Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36445392 Review.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of Crohn's disease in children and young adults: quantitative metric correlations and MRI disease severity associations.Pediatr Radiol. 2025 Jun;55(7):1425-1436. doi: 10.1007/s00247-025-06203-8. Epub 2025 Mar 13. Pediatr Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40080165 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of bowel wall thickening on ultrasound with pathological correlation in children.Pediatr Radiol. 2022 Aug;52(9):1786-1798. doi: 10.1007/s00247-022-05376-w. Epub 2022 May 6. Pediatr Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35513727 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging for Diagnosis and Assessment of Necrotizing Enterocolitis.Newborn (Clarksville). 2022 Jan-Mar;1(1):182-189. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-11002-0002. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Newborn (Clarksville). 2022. PMID: 36864828 Free PMC article.
-
Microbubbles in the belly: optimizing the protocol for contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the pediatric abdomen.Pediatr Radiol. 2023 Jun;53(7):1224-1236. doi: 10.1007/s00247-022-05464-x. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Pediatr Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36006474 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

