Detecting and Monitoring Hydrogels with Medical Imaging
- PMID: 33979137
- PMCID: PMC8440385
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01547
Detecting and Monitoring Hydrogels with Medical Imaging
Abstract
Hydrogels, water-swollen polymer networks, are being applied to numerous biomedical applications, such as drug delivery and tissue engineering, due to their potential tunable rheologic properties, injectability into tissues, and encapsulation and release of therapeutics. Despite their promise, it is challenging to assess their properties in vivo and crucial information such as hydrogel retention at the site of administration and in situ degradation kinetics are often lacking. To address this, technologies to evaluate and track hydrogels in vivo with various imaging techniques have been developed in recent years, including hydrogels functionalized with contrast generating material that can be imaged with methods such as X-ray computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), optical imaging, and nuclear imaging systems. In this review, we will discuss emerging approaches to label hydrogels for imaging, review the advantages and limitations of these imaging techniques, and highlight examples where such techniques have been implemented in biomedical applications.
Keywords: biomedical imaging; computed tomography; contrast agents; fluorescence imaging; hydrogels; magnetic resonance imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



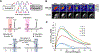



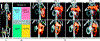
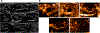
References
-
- Guvendiren M; Lu HD; Burdick JA Shear-thinning hydrogels for biomedical applications. Soft Matter 2012, 8 (2), 260–272.
-
- Hoffman AS Hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev 2012, 64, 18–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
