SO2 Capture Using Porous Organic Cages
- PMID: 33979473
- PMCID: PMC8361948
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202104555
SO2 Capture Using Porous Organic Cages
Abstract
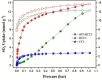
We report the first experimental investigation of porous organic cages (POCs) for the demanding challenge of SO2 capture. Three structurally related N-containing cage molecular materials were studied. An imine-functionalized POC (CC3) showed modest and reversible SO2 capture, while a secondary-amine POC (RCC3) exhibited high but irreversible SO2 capture. A tertiary amine POC (6FT-RCC3) demonstrated very high SO2 capture (13.78 mmol g-1 ; 16.4 SO2 molecules per cage) combined with excellent reversibility for at least 50 adsorption-desorption cycles. The adsorption behavior was investigated by FTIR spectroscopy, 13 C CP-MAS NMR experiments, and computational calculations.
Keywords: SO2; adsorption; chemical stability; porous organic cages.
© 2021 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): A.I.C. and M.L. have a financial interest in the start‐up company CageCapture Ltd, which is seeking to commercialize porous organic cages.
Figures



References
-
- Silva R. A., West J. J., Lamarque J.-F., Shindell D. T., Collins W. J., Faluvegi G., Folberth G. A., Horowitz L. W., Nagashima T., Naik V., Rumbold S. T., Sudo K., Takemura T., Bergmann D., Cameron-Smith P., Doherty R. M., Josse B., MacKenzie I. A., Stevenson D. S., Zeng G., Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 647–651. - PMC - PubMed
-
- None
-
- None
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

