Phase precession in the human hippocampus and entorhinal cortex
- PMID: 33979655
- PMCID: PMC8195854
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.017
Phase precession in the human hippocampus and entorhinal cortex
Abstract
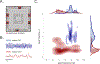
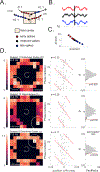
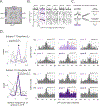
Knowing where we are, where we have been, and where we are going is critical to many behaviors, including navigation and memory. One potential neuronal mechanism underlying this ability is phase precession, in which spatially tuned neurons represent sequences of positions by activating at progressively earlier phases of local network theta oscillations. Based on studies in rodents, researchers have hypothesized that phase precession may be a general neural pattern for representing sequential events for learning and memory. By recording human single-neuron activity during spatial navigation, we show that spatially tuned neurons in the human hippocampus and entorhinal cortex exhibit phase precession. Furthermore, beyond the neural representation of locations, we show evidence for phase precession related to specific goal states. Our findings thus extend theta phase precession to humans and suggest that this phenomenon has a broad functional role for the neural representation of both spatial and non-spatial information.
Keywords: entorhinal cortex; frontal cortex; goal-directed navigation; hippocampus; phase precession; place cells; temporal coding; theta oscillations.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
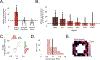

Comment in
-
Keep time to find your way.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021 Jul;22(7):385. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00476-2. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34075222 No abstract available.
References
-
- Aghajan ZM, Acharya L, Moore JJ, Cushman JD, Vuong C, & Mehta MR (2014). Impaired spatial selectivity and intact phase precession in two-dimensional virtual reality. Nature neuroscience. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y & Hochberg Y (1995). Controlling the False Discovery Rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of Royal Statistical Society, Series B, 57, 289–300.
-
- Bi G & Poo M (2001). Synaptic modification by correlated activity: Hebb’s postulate revisited. Annu Rev Neurosci, 24, 139–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

