DSCMF: prediction of LncRNA-disease associations based on dual sparse collaborative matrix factorization
- PMID: 33980147
- PMCID: PMC8114493
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-020-03868-w
DSCMF: prediction of LncRNA-disease associations based on dual sparse collaborative matrix factorization
Abstract
Background: In the development of science and technology, there are increasing evidences that there are some associations between lncRNAs and human diseases. Therefore, finding these associations between them will have a huge impact on our treatment and prevention of some diseases. However, the process of finding the associations between them is very difficult and requires a lot of time and effort. Therefore, it is particularly important to find some good methods for predicting lncRNA-disease associations (LDAs).
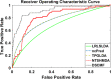
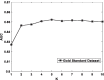
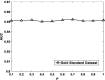
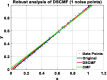
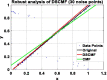
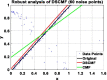
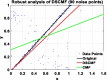
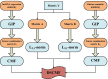
Results: In this paper, we propose a method based on dual sparse collaborative matrix factorization (DSCMF) to predict LDAs. The DSCMF method is improved on the traditional collaborative matrix factorization method. To increase the sparsity, the L2,1-norm is added in our method. At the same time, Gaussian interaction profile kernel is added to our method, which increase the network similarity between lncRNA and disease. Finally, the AUC value obtained by the experiment is used to evaluate the quality of our method, and the AUC value is obtained by the ten-fold cross-validation method.
Conclusions: The AUC value obtained by the DSCMF method is 0.8523. At the end of the paper, simulation experiment is carried out, and the experimental results of prostate cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer and colorectal cancer are analyzed in detail. The DSCMF method is expected to bring some help to lncRNA-disease associations research. The code can access the https://github.com/Ming-0113/DSCMF website.
Keywords: Collaborative matrix factorization; Gaussian interaction profile kernel; LncRNA-disease associations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multi-Label Fusion Collaborative Matrix Factorization for Predicting LncRNA-Disease Associations.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021 Mar;25(3):881-890. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2988720. Epub 2021 Mar 5. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021. PMID: 32324583
-
WGRCMF: A Weighted Graph Regularized Collaborative Matrix Factorization Method for Predicting Novel LncRNA-Disease Associations.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021 Jan;25(1):257-265. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2985703. Epub 2021 Jan 5. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021. PMID: 32287024
-
Prediction of lncRNA and disease associations based on residual graph convolutional networks with attention mechanism.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 2;14(1):5185. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55957-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38431702 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in machine learning methods for predicting LncRNA and disease associations.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Nov 30;12:1071972. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1071972. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36530425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RWSF-BLP: a novel lncRNA-disease association prediction model using random walk-based multi-similarity fusion and bidirectional label propagation.Mol Genet Genomics. 2021 May;296(3):473-483. doi: 10.1007/s00438-021-01764-3. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Mol Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33590345 Review.
Cited by
-
iLncDA-RSN: identification of lncRNA-disease associations based on reliable similarity networks.Front Genet. 2023 Aug 8;14:1249171. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1249171. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37614816 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting potential lncRNA biomarkers for lung cancer and neuroblastoma based on an ensemble of a deep neural network and LightGBM.Front Genet. 2023 Aug 16;14:1238095. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1238095. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37655066 Free PMC article.
-
GCNFORMER: graph convolutional network and transformer for predicting lncRNA-disease associations.BMC Bioinformatics. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05625-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38166659 Free PMC article.
-
LDA-SCGB: inferring lncRNA-disease associations based on condensed gradient boosting.BMC Bioinformatics. 2025 Jul 22;26(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s12859-025-06169-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40696287 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of lncRNA-disease association based on a Laplace normalized random walk with restart algorithm on heterogeneous networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Jan 4;23(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04538-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 34983367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez-Dominguez JR, Hu W, Lodish HF. Regulation of eukaryotic cell differentiation by long non-coding RNAs. In: Molecular biology of long non-coding RNAs. Springer; 2013. p. 15–67.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

