MYLK4 promotes tumor progression through the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in osteosarcoma
- PMID: 33980265
- PMCID: PMC8114533
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-01965-z
MYLK4 promotes tumor progression through the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in osteosarcoma
Abstract
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary bone cancer in adolescents and lung metastasis is the leading cause of death in patients with OS. However, the molecular mechanisms that promote OS growth and metastasis remain unknown.
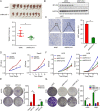
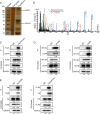
Methods: We investigated the expression of myosin light chain kinase family members between metastasis and non-metastasis patients in the TARGET database and ensured that only myosin light chain kinase family member 4 (MYLK4) had higher expression in metastatic osteosarcoma patients. Then we confirmed the results by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blotting (WB) of OS tissues. The effect of MYLK4 on the metastasis and proliferation of OS cells was investigated by wound healing, Transwell and colony-formation assays. Mass spectrum analysis was used to ensure the new binding protein of MYLK4. Tissue microarrays analysis was used to show the correlation between MYLK4 and pEGFR (Y1068). A series of in vivo experiments were conducted to reveal the mechanisms by which MYLK4 modulated the metastasis and proliferation of OS.
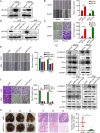
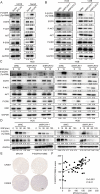
Results: Myosin Light Chain Kinase Family Member 4 (MYLK4) was significantly upregulated in metastatic human OS tissues. Growth and metastasis of OS could be accelerated by MYLK4 overexpression, whereas silencing MYLK4 expression resulted in decreased cell growth and metastasis. Mechanistically, mass spectrum analysis showed that MYLK4 interacted with the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in osteosarcoma cells and promoted growth and metastasis via the EGFR signaling pathway. Tissue microarrays analysis also showed that MYLK4 expression had a positive correlation with the expression of pEGFR (Y1068). Moreover, the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib could partially reverse the effect of cell proliferation and metastasis caused by MYLK4 overexpression. Importantly, the combination of MYLK4 and EGFR inhibitors had synergistic effects on growth and metastasis of OS in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that MYLK4 promotes OS growth and metastasis by activating the EGFR signaling pathway and can be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of OS patients.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor receptor; Growth; MYLK4; Metastasis; Osteosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The TGFβ-miR-499a-SHKBP1 pathway induces resistance to EGFR inhibitors in osteosarcoma cancer stem cell-like cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 28;38(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1195-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31138318 Free PMC article.
-
KIAA1429 promotes osteosarcoma progression by promoting stem cell properties and is regulated by miR-143-3p.Cell Cycle. 2020 May;19(10):1172-1185. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2020.1749465. Epub 2020 Apr 14. Cell Cycle. 2020. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2021 Dec;20(24):2666. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1971878. PMID: 32286148 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor promotes tumor progression and contributes to gemcitabine resistance in osteosarcoma.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Mar 2;53(3):317-324. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa177. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 33432347
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Canine Osteosarcoma Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 31;22(7):3639. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073639. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of pre-metastatic niches induced by osteosarcoma-derived extracellular vesicles in lung metastasis: A potential opportunity for diagnosis and intervention.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Sep;178:117203. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117203. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39067163 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of Pip4k2c confers liver-metastatic organotropism through insulin-dependent PI3K-AKT pathway activation.Nat Cancer. 2024 Mar;5(3):433-447. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00704-x. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Nat Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38286827 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenomic response to albuterol treatment in asthma-relevant airway epithelial cells.Clin Epigenetics. 2023 Oct 3;15(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01571-0. Clin Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37784136 Free PMC article.
-
Chlorinated benzothiadiazines inhibit angiogenesis through suppression of VEGFR2 phosphorylation.Bioorg Med Chem. 2022 Aug 1;67:116805. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2022.116805. Epub 2022 May 15. Bioorg Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35635929 Free PMC article.
-
Hub biomarkers in ultrasound-guided bladder cancer and osteosarcoma: Myosin light chain kinase and caldesmon.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 1;102(48):e36414. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036414. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38050320 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian disruption dysregulates lung gene expression associated with inflammatory lung injury.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 14;15:1348181. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1348181. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38558813 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

