Improving iron folic acid consumption through interpersonal communication: Findings from the Reduction in Anemia through Normative Innovations (RANI) project
- PMID: 33980397
- PMCID: PMC8710582
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pec.2021.04.032
Improving iron folic acid consumption through interpersonal communication: Findings from the Reduction in Anemia through Normative Innovations (RANI) project
Abstract
Objective: More than half of Indian women of reproductive age are anemic. Regular iron folic acid uptake can prevent and treat anemia. This study investigated the effect of interpersonal communication on improving IFA use among women of reproductive age.
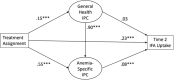
Methods: The Reduction in Anemia through Normative Innovations (RANI) Project is a cluster randomized trial that collected longitudinal data from control (n = 1896) and intervention (n = 1898) communities in Odisha, India at Time 1 and six months later at Time 2. Structural equation models assessed the effect of the intervention on iron folic acid use via multiple interpersonal communication pathways.
Results: Compared to the control arm, iron folic acid use significantly increased in the intervention arm. Both, general health interpersonal communication and anemia-specific interpersonal communication were augmented in the intervention communities. The impact of the intervention on iron folic acid use was mediated through anemia-specific interpersonal communication.
Conclusion: The RANI Project increased interpersonal communication among participants, resulting in increased iron folic acid use for anemia reduction.
Practice implications: Strategic use of targeted interpersonal communication to promote behavior change appears to be a viable strategy to increase iron folic acid use to reduce anemia.
Keywords: Anemia; Interpersonal communication; Intervention; Iron folic acid; Women of reproductive age.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) and ICF, National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4), India, 2015–16: Odisha. Mumbai: IIPS., 2017. (n.d.).
-
- i ANEMIA MUKT BHARAT-OPERATIONAL GUIDELINES Operational Guidelines for Programme Managers INTENSIFIED NATIONAL IRON PLUS INITIATIVE (I-NIPI) Ministry of Health and Family Welfare Government of India, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

