Mucosal immunity-mediated modulation of the gut microbiome by oral delivery of probiotics into Peyer's patches
- PMID: 33980483
- PMCID: PMC8115924
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abf0677
Mucosal immunity-mediated modulation of the gut microbiome by oral delivery of probiotics into Peyer's patches
Erratum in
-
Erratum for the Research Article: "Mucosal immunity mediated modulation of the gut microbiome by oral delivery of probiotics into Peyer's patches".Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 11;8(6):eabo0538. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abo0538. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35148190 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
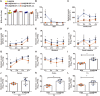
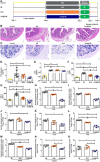
Methods capable of maintaining gut microbiota homeostasis to prevent bacterial translocation and infection under external threats are critical for multiple facets of human health but have been rarely reported. Here, we describe the elicitation of mucosal immunity to modulate the gut microbiota by oral delivery of living probiotics into Peyer's patches. Probiotics are individually camouflaged within a yeast membrane, on which the embedded β-glucan can facilitate the phagocytosis of microfold cells that locate in the intestinal epithelium. The delivery of probiotics into lymphoid follicles after oral ingestion promotes robust mucosal immune responses and notably upgrades the production of secretory immunoglobulin A. The provoked immunity positively regulates the gut microflora, which, in turn, retains gut homeostasis and provides defense against environmental attacks. In two murine models of gut barrier impairment, oral administration with camouflaged probiotics effectively prevents the breakdown of intestinal barrier and evidences limited bacterial translocation and systemic inflammation.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures






References
-
- Gentile C. L., Weir T. L., The gut microbiota at the intersection of diet and human health. Science 362, 776–780 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Gu Y., Wang X., Li J., Zhang Y., Zhong H., Liu R., Zhang D., Feng Q., Xie X., Hong J., Ren H., Liu W., Ma J., Su Q., Zhang H., Yang J., Wang X., Zhao X., Gu W., Bi Y., Peng Y., Xu X., Xia H., Li F., Xu X., Yang H., Xu G., Madsen L., Kristiansen K., Ning G., Wang W., Analyses of gut microbiota and plasma bile acids enable stratification of patients for antidiabetic treatment. Nat. Commun. 8, 1785 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roy S., Trinchieri G., Microbiota: A key orchestrator of cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17, 271–285 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

