Forced into an ecological corner: Round-the-clock deep foraging on small prey by elephant seals
- PMID: 33980496
- PMCID: PMC8115928
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg3628
Forced into an ecological corner: Round-the-clock deep foraging on small prey by elephant seals
Abstract
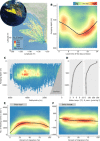
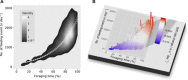
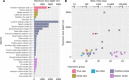
Small mesopelagic fishes dominate the world's total fish biomass, yet their ecological importance as prey for large marine animals is poorly understood. To reveal the little-known ecosystem dynamics, we identified prey, measured feeding events, and quantified the daily energy balance of 48 deep-diving elephant seals throughout their oceanic migrations by leveraging innovative technologies: animal-borne smart accelerometers and video cameras. Seals only attained positive energy balance after feeding 1000 to 2000 times per day on small fishes, which required continuous deep diving (80 to 100% of each day). Interspecies allometry suggests that female elephant seals have exceptional diving abilities relative to their body size, enabling them to exploit a unique foraging niche on small but abundant mesopelagic fish. This unique foraging niche requires extreme round-the-clock deep diving, limiting the behavioral plasticity of elephant seals to a changing mesopelagic ecosystem.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures

References
-
- Martin A., Boyd P., Buesseler K., Cetinic I., Claustre H., Giering S., Henson S., Irigoien X., Kriest I., Memery L., Robinson C., Saba G., Sanders R., Siegel D., Villa-Alfageme M., Guidi L., The oceans’ twilight zone must be studied now, before it is too late. Nature 580, 26–28 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Irigoien X., Klevjer T. A., Røstad A., Martinez U., Boyra G., Acuña J. L., Bode A., Echevarria F., Gonzalez-Gordillo J. I., Hernandez-Leon S., Agusti S., Aksnes D. L., Duarte C. M., Kaartvedt S., Large mesopelagic fishes biomass and trophic efficiency in the open ocean. Nat. Commun. 5, 3271 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yoshino K., Takahashi A., Adachi T., Costa D. P., Robinson P. W., Peterson S. H., Hückstädt L. A., Holser R. R., Naito Y., Acceleration-triggered animal-borne videos show a dominance of fish in the diet of female northern elephant seals. J. Exp. Biol. 223, jeb212936 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Goetsch C., Conners M. G., Budge S. M., Mitani Y., Walker W. A., Bromaghin J. F., Simmons S. E., Reichmuth C., Costa D. P., Energy-rich mesopelagic fishes revealed as a critical prey resource for a deep-diving predator using quantitative fatty acid signature analysis. Front. Mar. Sci. 5, 430 (2018).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

