Modification of maternal late pregnancy sleep position: a survey evaluation of a New Zealand public health campaign
- PMID: 33980531
- PMCID: PMC8118030
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-047681
Modification of maternal late pregnancy sleep position: a survey evaluation of a New Zealand public health campaign
Abstract
Introduction: A 'Sleep-On-Side When Baby's Inside' public health campaign was initiated in New Zealand in 2018. This was in response to evidence that maternal supine going-to-sleep position was an independent risk factor for stillbirth from 28 weeks' gestation. We evaluated the success of the campaign on awareness and modification of late pregnancy going-to-sleep position through nationwide surveys.
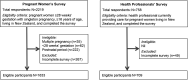
Methods and analysis: Two web-based cross-sectional surveys were conducted over 12 weeks in 2019-2020 in a sample of (1) pregnant women ≥28 weeks, primary outcome of going-to-sleep position; and (2) health professionals providing pregnancy care, primary outcome of knowledge of going-to-sleep position and late stillbirth risk. Univariable logistic regression was performed to identify factors associated with supine going-to-sleep position.
Discussion: The survey of pregnant women comprised 1633 eligible participants. Going-to-sleep position last night was supine (30, 1.8%), non-supine (1597, 97.2%) and no recall (16, 1.0%). Supine position had decreased from 3.9% in our previous New Zealand-wide study (2012-2015). Most women (1412, 86.5%) had received sleep-on-side advice with no major resultant worry (1276, 90.4%). Two-thirds (918, 65.0%) had changed their going-to-sleep position based on advice, with most (611 of 918, 66.5%) reporting little difficulty. Supine position was associated with Māori (OR 5.05, 95% CI 2.10 to 12.1) and Asian-non-Indian (OR 4.20, 95% CI 1.27 to 13.90) ethnicity; single (OR 10.98, 95% CI 4.25 to 28.42) and cohabitating relationship status (OR 2.69, 95% CI 1.09 to 6.61); hospital-based maternity provider (OR 2.55, 95% CI 1.07 to 6.10); education overseas (OR 3.92, 95% CI 1.09 to 14.09) and primary-secondary level (OR 2.80, 95% CI 1.32 to 6.08); and not receiving sleep-on-side advice (OR 6.70, 95% CI 3.23 to 13.92). The majority of health professionals (709 eligible participants) reported awareness of supine going-to-sleep position and late stillbirth risk (543, 76.6%).
Conclusion: Most pregnant women had received and implemented sleep-on-side advice without major difficulty or concern. Some groups of women may need a tailored approach to acquisition of going-to-sleep position information.
Keywords: obstetrics; paediatrics; primary care; public health; sleep medicine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- PMMRC . Te Pūrongo ā-Tau Tekau mā Toru O te Komiti Arotake mate Pēpi, mate Whaea Hoki. Thirteenth annual report of the perinatal and maternal mortality review Committee: te tuku pūrongo mō te mate me te whakamate 2017. reporting mortality and morbidity 2017. Wellington: Health Quality & Safety Commission, New Zealand Government, 2019.
-
- Humphries A, Ali Mirjalili S, Tarr GP. The effect of supine positioning on maternal hemodynamics during late pregnancy. J Maternal-Fetal Neonat Med 2018:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical