Waterpipe smoking: a review of pulmonary and health effects
- PMID: 33980668
- PMCID: PMC9488736
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0374-2020
Waterpipe smoking: a review of pulmonary and health effects
Abstract
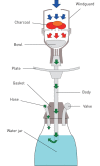
Waterpipe smoking is an old form of tobacco smoking, originating in Persia and the Middle East. The popularity of the waterpipe is increasing worldwide, particularly among young adults, and there are widespread misconceptions regarding its negative health effects. The inhaled smoke of the waterpipe contain several toxic and hazardous materials including nicotine, tar, polyaromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals, all of which are proven to be related to lung diseases and cancer. Regular waterpipe smoking is associated with respiratory symptoms, a decrease in pulmonary function and increased risk for lung disease such as COPD. Additional negative health effects include increased risk for arterial stiffness, ischaemic heart disease and several cancer types including lung cancer. This review summarises the negative health effects of waterpipe smoking, with emphasis on cardiorespiratory complications. Increased awareness and knowledge amongst healthcare professionals will hopefully help identify waterpipe smokers and promote patient education. Applying World Health Organization (WHO) regulations will provide a synergistic effect in reducing waterpipe use and associated disease.
Copyright ©The authors 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: F. Darawshy has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Abu Rmeileh has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R. Kuint has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N. Berkman has nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (US) Office on Smoking and Health. The Health Consequences of Smoking – 50 Years of Progress a Report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US), 2014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources