A Cytopathic Effect-Based Tissue Culture Method for HCoV-OC43 Titration Using TMPRSS2-Expressing VeroE6 Cells
- PMID: 33980675
- PMCID: PMC8125049
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00159-21
A Cytopathic Effect-Based Tissue Culture Method for HCoV-OC43 Titration Using TMPRSS2-Expressing VeroE6 Cells
Abstract
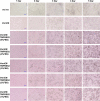
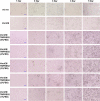
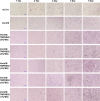
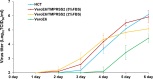
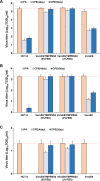
Human coronavirus (HCoV)-OC43 rarely shows a cytopathic effect (CPE) after infection of various cell lines, and the indirect immunoperoxidase assay (IPA), a relatively complex procedure, has long been used as an alternative assay. Because HCoV-OC43 uses cell-surface transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2) for cell entry, VeroE6 cells expressing TMPRSS2 may show a clear CPE after HCoV-OC43 infection. The aim of this study was to construct a 50% tissue culture infectious dose (TCID50) assay for HCoV-OC43 based on CPE evaluation using VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells. VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells showed clear CPEs 3 to 4 days after low-titer HCoV-OC43 infection. Evaluation of viral kinetics indicated that the viral titer in the culture supernatant of VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells in the early stages of infection was higher than that of other cells. In comparison, between the CPE-based and the IPA-based (i.e., the reference titer) methods, the titer measured with CPE evaluation 4 to 5 days after infection using VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells showed a much smaller difference from the reference titer than that measured using other cells. Thus, the TCID50 assay using CPE evaluation with VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells provides the correct titer value and will greatly contribute to future research on HCoV-OC43.IMPORTANCE HCoV-OC43 rarely shows a cytopathic effect (CPE) in infected cell lines, and thus the plaque and TCID50 assays by CPE observation are not applicable for titration; the indirect immunoperoxidase assay (IPA) is used instead. However, the IPA is relatively complex, time-consuming, costly, and not suitable for simultaneous titration of many samples. We developed a TCID50 assay using CPE evaluation with TMPRSS2-expressing VeroE6/TMPRSS2 cells that provides the same accuracy as the conventional IPA-based viral titration and does not require any staining procedures using antibodies or substrates. This titration method will greatly contribute to future research on HCoV-OC43 by allowing simple, low-cost, and accurate titration of this virus.
Keywords: 50% tissue culture infectious dose assay; HCoV-OC43; TMPRSS2; cytopathic effect; human coronavirus; titration.
Copyright © 2021 Hirose et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improving human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43) research comparability in studies using HCoV-OC43 as a surrogate for SARS-CoV-2.J Virol Methods. 2022 Jan;299:114317. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2021.114317. Epub 2021 Oct 9. J Virol Methods. 2022. PMID: 34634321 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of the propagation and plaque titration conditions for human coronavirus OC43 as a surrogate for SARS-CoV-2.Arch Virol. 2024 Oct 4;169(10):214. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-06146-9. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 39365483
-
Titration of human coronaviruses, HcoV-229E and HCoV-OC43, by an indirect immunoperoxidase assay.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;454:93-102. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-181-9_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 19057861 Free PMC article.
-
TMPRSS2 in microbial interactions: Insights from HKU1 and TcsH.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Nov 20;20(11):e1012677. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012677. eCollection 2024 Nov. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39565778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 cytopathic effect (CPE).SARS-CoV-2 Assays [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS); 2020–. SARS-CoV-2 Assays [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS); 2020–. PMID: 35512046 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Environmental Stability and Disinfectant Effectiveness for Human Coronavirus OC43 on Human Skin Surface.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 22;11(2):e0238122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02381-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36840603 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Use of Tea Tree Oil as a Disinfectant Agent against Coronaviruses: A Combined Experimental and Simulation Study.Molecules. 2022 Jun 12;27(12):3786. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123786. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744913 Free PMC article.
-
Seasonal human coronaviruses OC43, 229E, and NL63 induce cell surface modulation of entry receptors and display host cell-specific viral replication kinetics.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Jul 2;12(7):e0422023. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04220-23. Epub 2024 Jun 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38864599 Free PMC article.
-
Cytopathic Effect Assay and Plaque Assay to Evaluate in vitro Activity of Antiviral Compounds Against Human Coronaviruses 229E, OC43, and NL63.Bio Protoc. 2022 Feb 5;12(3):e4314. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4314. eCollection 2022 Feb 5. Bio Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35284599 Free PMC article.
-
Immunodetection assays for the quantification of seasonal common cold coronaviruses OC43, NL63, or 229E infection confirm nirmatrelvir as broad coronavirus inhibitor.Antiviral Res. 2022 Jul;203:105343. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105343. Epub 2022 May 19. Antiviral Res. 2022. PMID: 35598779 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Hoek L. 2007. Human coronaviruses: what do they cause? Antivir Ther 12:651–658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
