Tools and Techniques for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 Detection
- PMID: 33980687
- PMCID: PMC8142517
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00228-20
Tools and Techniques for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 Detection
Abstract
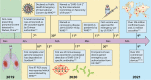
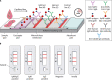
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, caused by severe acute respiratory disease coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has led to millions of confirmed cases and deaths worldwide. Efficient diagnostic tools are in high demand, as rapid and large-scale testing plays a pivotal role in patient management and decelerating disease spread. This paper reviews current technologies used to detect SARS-CoV-2 in clinical laboratories as well as advances made for molecular, antigen-based, and immunological point-of-care testing, including recent developments in sensor and biosensor devices. The importance of the timing and type of specimen collection is discussed, along with factors such as disease prevalence, setting, and methods. Details of the mechanisms of action of the various methodologies are presented, along with their application span and known performance characteristics. Diagnostic imaging techniques and biomarkers are also covered, with an emphasis on their use for assessing COVID-19 or monitoring disease severity or complications. While the SARS-CoV-2 literature is rapidly evolving, this review highlights topics of interest that have occurred during the pandemic and the lessons learned throughout. Exploring a broad armamentarium of techniques for detecting SARS-CoV-2 will ensure continued diagnostic support for clinicians, public health, and infection prevention and control for this pandemic and provide advice for future pandemic preparedness.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; COVID-19; NAAT; PCR; SARS-CoV-2; antigen; biomarkers; coronavirus; next-generation sequencing; serology.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures











References
-
- LeBlanc JJ, Li Y, Bastien N, Forward KR, Davidson RJ, Hatchette TF. 2009. Switching gears for an influenza pandemic: validation of a duplex reverse transcriptase PCR assay for simultaneous detection and confirmatory identification of pandemic (H1N1) 2009 influenza virus. J Clin Microbiol 47:3805–3813. 10.1128/JCM.01344-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, Bi Y, Ma X, Zhan F, Wang L, Hu T, Zhou H, Hu Z, Zhou W, Zhao L, Chen J, Meng Y, Wang J, Lin Y, Yuan J, Xie Z, Ma J, Liu WJ, Wang D, Xu W, Holmes EC, Gao GF, Wu G, Chen W, Shi W, Tan W. 2020. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 395:565–574. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

