Critical Determinants of Cytokine Storm and Type I Interferon Response in COVID-19 Pathogenesis
- PMID: 33980688
- PMCID: PMC8142516
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00299-20
Critical Determinants of Cytokine Storm and Type I Interferon Response in COVID-19 Pathogenesis
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Ramasamy and Subbian, "Critical Determinants of Cytokine Storm and Type I Interferon Response in COVID-19 Pathogenesis".Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021 Dec 15;34(4):e0016321. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00163-21. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34259566 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
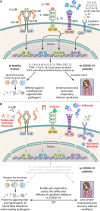
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a rapidly evolving pandemic worldwide with at least 68 million COVID-19-positive cases and a mortality rate of about 2.2%, as of 10 December 2020. About 20% of COVID-19 patients exhibit moderate to severe symptoms. Severe COVID-19 manifests as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) with elevated plasma proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin 1β (IL-1β), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10/IP10), macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha (MIP-1α), and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2), with low levels of interferon type I (IFN-I) in the early stage and elevated levels of IFN-I during the advanced stage of COVID-19. Most of the severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients have had preexisting comorbidities, including hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory diseases. These conditions are known to perturb the levels of cytokines, chemokines, and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), an essential receptor involved in SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host cells. ACE2 downregulation during SARS-CoV-2 infection activates the angiotensin II/angiotensin receptor (AT1R)-mediated hypercytokinemia and hyperinflammatory syndrome. However, several SARS-CoV-2 proteins, including open reading frame 3b (ORF3b), ORF6, ORF7, ORF8, and the nucleocapsid (N) protein, can inhibit IFN type I and II (IFN-I and -II) production. Thus, hyperinflammation, in combination with the lack of IFN responses against SARS-CoV-2 early on during infection, makes the patients succumb rapidly to COVID-19. Therefore, therapeutic approaches involving anti-cytokine/anti-cytokine-signaling and IFN therapy would favor the disease prognosis in COVID-19. This review describes critical host and viral factors underpinning the inflammatory "cytokine storm" induction and IFN antagonism during COVID-19 pathogenesis. Therapeutic approaches to reduce hyperinflammation and their limitations are also discussed.
Keywords: ACE2; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; cell surface receptors; comorbidities; inflammation; innate immunity; interferon; intracellular signaling; proinflammatory cytokines.
Copyright © 2021 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


References
-
- Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, Chen Y-M, Wang W, Song Z-G, Hu Y, Tao Z-W, Tian J-H, Pei Y-Y, Yuan M-L, Zhang Y-L, Dai F-H, Liu Y, Wang Q-M, Zheng J-J, Xu L, Holmes EC, Zhang Y-Z. 2020. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 579:265–269. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H, Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, Bi Y, Ma X, Zhan F, Wang L, Hu T, Zhou H, Hu Z, Zhou W, Zhao L, Chen J, Meng Y, Wang J, Lin Y, Yuan J, Xie Z, Ma J, Liu WJ, Wang D, Xu W, Holmes EC, Gao GF, Wu G, Chen W, Shi W, Tan W. 2020. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 395:565–574. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

