Difference in the Source of Anti-AQP4-IgG and Anti-MOG-IgG Antibodies in CSF in Patients With Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 33980704
- PMCID: PMC8312856
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012175
Difference in the Source of Anti-AQP4-IgG and Anti-MOG-IgG Antibodies in CSF in Patients With Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
Objective: To elucidate the differences in the source and in the level of intrathecal synthesis between anti-aquaporin-4 antibodies (AQP4-IgG) and anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibodies (MOG-IgG).
Methods: Thirty-eight patients with MOG-IgG-associated disease and 36 with AQP4-IgG-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD) were studied for the antibody titers in the sera and CSF simultaneously collected in the acute attacks. The quotients between CSF and serum levels of albumin, total immunoglobulin G, and each disease-specific antibody were calculated. Intrathecal production level in each disease-specific antibody was evaluated by calculating the antibody index from these quotients.
Results: Eleven of the 38 patients with MOG-IgG were positive for the antibody only in the CSF, while no patient with AQP4-IgG showed CSF-restricted AQP4-IgG. Blood-brain barrier compromise as shown by raised albumin quotients was seen in 75.0% of MOG-IgG-positive cases and 43.8% of AQP4-IgG-positive cases. Moreover, MOG-IgG quotients were >10 times higher than AQP4-IgG quotients (effect size r = 0.659, p < 0.0001). Elevated antibody index (>4.0) was confirmed in 12 of 21 with MOG-IgG, whereas it was seen only in 1 of 16 with AQP4-IgG (φ = 0.528, p < 0.0001). The CSF MOG-IgG titers (ρ = 0.519, p = 0.001) and antibody indexes for MOG-IgG (ρ = 0.472, p = 0.036) correlated with the CSF cell counts but not with clinical disability.
Conclusions: Intrathecal production of MOG-IgG may occur more frequently than that of AQP4-IgG. This finding implies the different properties of B-cell trafficking and antibody production between MOG-IgG-associated disease and AQP4-IgG-positive NMOSD.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
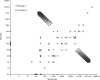
 ) and immunoglobulin G quotient (
) and immunoglobulin G quotient ( ) on the Reibergram. Plots in patients with anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody (MOG-IgG) or anti–aquaporin-4 antibodies (AQP4-IgG) distribute below and along the upper line of the distribution of patients without intrathecal IgG synthesis on the Reibergram (
) on the Reibergram. Plots in patients with anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody (MOG-IgG) or anti–aquaporin-4 antibodies (AQP4-IgG) distribute below and along the upper line of the distribution of patients without intrathecal IgG synthesis on the Reibergram ( ) line, whereas many of them were with raised
) line, whereas many of them were with raised  . (B) Scatterplots with
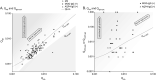
. (B) Scatterplots with  and quotient for each specific antibody (i.e.,
and quotient for each specific antibody (i.e.,  ,
,  ) (
) ( ) on the Reibergram. Plots in patients with MOG-IgG distribute above the
) on the Reibergram. Plots in patients with MOG-IgG distribute above the  line and not along the line. MS = multiple sclerosis.
line and not along the line. MS = multiple sclerosis.
 ,
,  ) (
) ( ), and (C) antibody index (AI) are shown. IgG index reflects the intrathecal total IgG production, whereas
), and (C) antibody index (AI) are shown. IgG index reflects the intrathecal total IgG production, whereas  and AI represent the intrathecal production of each specific antibody. AQP4-IgG = anti–aquaporin-4 antibodies; MS = multiple sclerosis; MOG-IgG = anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody.
and AI represent the intrathecal production of each specific antibody. AQP4-IgG = anti–aquaporin-4 antibodies; MS = multiple sclerosis; MOG-IgG = anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody.
 = quotient for each specific antibody (i.e.,
= quotient for each specific antibody (i.e.,  ,
,  );
);  = upper line of the distribution of patients without intrathecal IgG synthesis on the Reibergram.
= upper line of the distribution of patients without intrathecal IgG synthesis on the Reibergram.Comment in
-
Intrathecal Production of MOG-IgG: Highlighting the Need for CSF Testing in Clinical Practice.Neurology. 2021 Jul 6;97(1):12-13. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000012177. Epub 2021 May 12. Neurology. 2021. PMID: 33980706 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
CSF cytokine profile in MOG-IgG+ neurological disease is similar to AQP4-IgG+ NMOSD but distinct from MS: a cross-sectional study and potential therapeutic implications.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018 Sep;89(9):927-936. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-317969. Epub 2018 Jun 6. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29875186 Free PMC article.
-
MOG-IgG in NMO and related disorders: a multicenter study of 50 patients. Part 1: Frequency, syndrome specificity, influence of disease activity, long-term course, association with AQP4-IgG, and origin.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Sep 26;13(1):279. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0717-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27788675 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders with antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein or aquaporin-4: Clinical and paraclinical characteristics in Algerian patients.J Neurol Sci. 2017 Oct 15;381:240-244. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2017.08.3254. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Neurol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28991690
-
Comparison of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-antibody disease and AQP4-IgG-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) when they co-exist with anti-NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor encephalitis.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2018 Feb;20:144-152. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2018. PMID: 29414288 Review.
-
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: Pathogenesis, treatment, and experimental models.Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019 Jan;27:412-418. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2018.12.002. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019. PMID: 30530071 Review.
Cited by
-
The Percentage of Neutrophils is Independently Associated with Blood-Brain Barrier(BBB) Disruption in Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein Antibody Associated Disease (MOGAD).J Inflamm Res. 2025 Feb 25;18:2823-2836. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S501150. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40026312 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin type-1 receptor and ACE2 autoantibodies in Parkinson´s disease.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022 Jun 14;8(1):76. doi: 10.1038/s41531-022-00340-9. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2022. PMID: 35701430 Free PMC article.
-
Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein-Immunoglobulin G in the CSF: Clinical Implication of Testing and Association With Disability.Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021 Oct 28;9(1):e1095. doi: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000001095. Print 2022 Jan. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2021. PMID: 34711644 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody disease.Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 28;14:1137998. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1137998. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36925938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Features and Imaging Findings of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein-IgG-Associated Disorder (MOGAD).Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 15;14:850743. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.850743. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35370624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
