Effect of CTLA4-Ig on Obliterative Bronchiolitis in a Mouse Intrapulmonary Tracheal Transplantation Model
- PMID: 33980752
- PMCID: PMC8684841
- DOI: 10.5761/atcs.oa.20-00398
Effect of CTLA4-Ig on Obliterative Bronchiolitis in a Mouse Intrapulmonary Tracheal Transplantation Model
Abstract
Objectives: One of the serious problems after lung transplantation is chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD). Most CLAD patients pathologically characterized by obliterative bronchiolitis (OB). Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA4)-Ig is a combination protein of the Fc fragment of human IgG1 linked to the extracellular domain of CTLA4. The aim of the study was to examine the effect of CTLA4-Ig therapy on OB using a mouse intrapulmonary tracheal transplantation (IPTT) model.
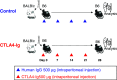
Methods: IPTT was performed between BALB/c (donor) and C57BL/6 (recipient) mice. Abatacept, which is a commercially available form of CTLA4-Ig, was intraperitoneally injected in recipient mice immediately after surgery, on days 7, 14, and 21. The mice in the control group received human IgG.
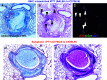
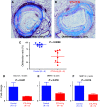
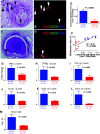
Results: We performed semi-quantitative analysis of graft luminal obliteration at post-transplant day 28. We calculated the obliteration ratio of the lumen of the transplanted trachea in each case. The obliteration ratio was significantly lower in the CTLA4-Ig group than that in the control group (91.2 ± 2.1% vs. 47.8 ± 7.9%, p = 0.0008). Immunofluorescent staining revealed significantly decreased lymphoid neogenesis in the lung.
Conclusions: CTLA4-Ig therapy attenuated tracheal obliteration with fibrous tissue in the mouse IPTT model. The attenuation of fibrous obliteration was correlated with the inhibition of lymphoid neogenesis.
Keywords: chronic lung allograft dysfunction; cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; lung transplantation; obliterative bronchiolitis.
Figures
References
-
- Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Goldfarb SB, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-fifth adult lung and heart-lung transplant report—2018. Focus theme: Multiorgan Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2018; 37: 1169– 83. - PubMed
-
- Verleden GM, Glanville AR, Lease ED, et al. Chronic lung allograft dysfunction: definition, diagnostic criteria, and approaches to treatment—A consensus report from the Pulmonary Council of the ISHLT. J Heart Lung Transplant 2019; 38: 493– 503. - PubMed
-
- Matsumura Y, Zuo XJ, Prehn J, et al. Soluble CTLA4Ig modifies parameters of acute inflammation in rat lung allograft rejection without altering lymphocytic infiltration or transcription of key cytokines. Transplantation 1995; 59: 551– 8. - PubMed
-
- Vincenti F, Rostaing L, Grinyo J, et al. Belatacept and long-term outcomes in kidney transplantation. N Engl J Med 2016; 374: 333– 43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

