Serotonergic signals enhanced hamster sperm hyperactivation
- PMID: 33980767
- PMCID: PMC8423610
- DOI: 10.1262/jrd.2020-108
Serotonergic signals enhanced hamster sperm hyperactivation
Abstract
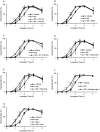
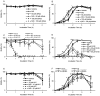
In the present study, we investigated the regulatory mechanisms underlying sperm hyperactivation enhanced by 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in hamsters. First, we examined the types of 5-HT receptors that regulate hyperactivation. Hyperactivation was significantly enhanced by 5-HT2A and 5-HT4 receptor agonists. Moreover, the results of the motility assay revealed that 5-HT2A, 5-HT3, and 5-HT4 receptor agonists significantly decreased the velocity and/or amplitude of sperm. Under 5-HT2 receptor stimulation, hyperactivation was associated with phospholipase C (PLC), inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptor, soluble adenylate cyclase (sAC), and protein kinase A (PKA). In contrast, under 5-HT4 receptor stimulation, hyperactivation was associated with transmembrane adenylate cyclase (tmAC), sAC, PKA, and CatSper channels. Accordingly, under the condition that sperm are hyperactivated, 5-HT likely stimulates PLC/IP3 receptor signals via the 5-HT2A receptor and tmAC/PKA/CatSper channel signals via the 5-HT4 receptor. After sAC and PKA are activated by these stimulations, sperm hyperactivation is enhanced.
Keywords: 5-HT2 receptor; 5-HT4 receptor; 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT); Hyperactivation; Sperm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures




References
-
- Yanagimachi R. Mammalian fertilization. In: Knobil E, Neill JD (ed.), The Physiology of Reproduction Vol. 2, 2nd ed. New York: Raven Press; 1994: 189–317.
-
- Fujinoki M. Melatonin-enhanced hyperactivation of hamster sperm. Reproduction 2008; 136: 533–541. - PubMed
-
- Langlais J, Roberts KD. A molecular membrane model of sperm capacitation and the acrosome reaction of mammalian spermatozoa. Gamete Res 1985; 12: 183–224.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

