Mitochondrial fission and mitophagy are independent mechanisms regulating ischemia/reperfusion injury in primary neurons
- PMID: 33980811
- PMCID: PMC8115279
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03752-2
Mitochondrial fission and mitophagy are independent mechanisms regulating ischemia/reperfusion injury in primary neurons
Abstract
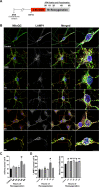
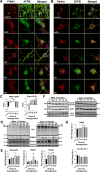
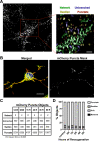
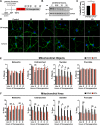
Mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy are constitutive and complex systems that ensure a healthy mitochondrial network through the segregation and subsequent degradation of damaged mitochondria. Disruption of these systems can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction and has been established as a central mechanism of ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Emerging evidence suggests that mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy are integrated systems; however, the role of this relationship in the context of I/R injury remains unclear. To investigate this concept, we utilized primary cortical neurons isolated from the novel dual-reporter mitochondrial quality control knockin mice (C57BL/6-Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1(CAG-mCherry/GFP)Ganl/J) with conditional knockout (KO) of Drp1 to investigate changes in mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagic flux during in vitro I/R injury. Mitochondrial dynamics was quantitatively measured in an unbiased manner using a machine learning mitochondrial morphology classification system, which consisted of four different classifications: network, unbranched, swollen, and punctate. Evaluation of mitochondrial morphology and mitophagic flux in primary neurons exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) and reoxygenation (OGD/R) revealed extensive mitochondrial fragmentation and swelling, together with a significant upregulation in mitophagic flux. Furthermore, the primary morphology of mitochondria undergoing mitophagy was classified as punctate. Colocalization using immunofluorescence as well as western blot analysis revealed that the PINK1/Parkin pathway of mitophagy was activated following OGD/R. Conditional KO of Drp1 prevented mitochondrial fragmentation and swelling following OGD/R but did not alter mitophagic flux. These data provide novel evidence that Drp1 plays a causal role in the progression of I/R injury, but mitophagy does not require Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PTEN-induced kinase 1-induced dynamin-related protein 1 Ser637 phosphorylation reduces mitochondrial fission and protects against intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Apr 21;26(15):1758-1774. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1758. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32351292 Free PMC article.
-
Interdependence of Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy and Mitochondrial Fission in Adult Mouse Hearts.Circ Res. 2015 Jul 31;117(4):346-51. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.306859. Epub 2015 Jun 2. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 26038571 Free PMC article.
-
ZFP36 protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced mitochondrial fragmentation and neuronal apoptosis through inhibiting NOX4-DRP1 pathway.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Feb;179:57-67. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.12.003. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 34896479
-
SUMOylation targeting mitophagy in cardiovascular diseases.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Nov;100(11):1511-1538. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02258-4. Epub 2022 Sep 26. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36163375 Review.
-
The role of Drp1 in mitophagy and cell death in the heart.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020 May;142:138-145. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.04.015. Epub 2020 Apr 14. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32302592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Incorporating machine learning and PPI networks to identify mitochondrial fission-related immune markers in abdominal aortic aneurysms.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 26;10(7):e27989. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27989. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38590878 Free PMC article.
-
Age and sex-specific changes in mitochondrial quality control in skeletal and cardiac muscle.Front Aging. 2025 Jun 25;6:1606110. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1606110. eCollection 2025. Front Aging. 2025. PMID: 40636717 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamin-related protein 1 is decreased and the mitochondrial network is altered in Friedreich's ataxia cardiomyopathy.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2022 Feb;143:106137. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2021.106137. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34923139 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothermia regulates mitophagy and apoptosis via PINK1/Parkin-VDAC 3 signaling pathway during oxygen-glucose deprivation/recovery injury.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 7;15(1):4607. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89176-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39920327 Free PMC article.
-
Agent-based modeling of neuronal mitochondrial dynamics using intrinsic variables of individual mitochondria.iScience. 2025 Apr 8;28(5):112390. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112390. eCollection 2025 May 16. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40330889 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

