C646 inhibits G2/M cell cycle-related proteins and potentiates anti-tumor effects in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 33980911
- PMCID: PMC8115044
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89530-8
C646 inhibits G2/M cell cycle-related proteins and potentiates anti-tumor effects in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
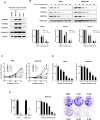
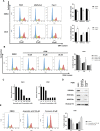
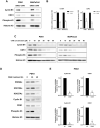
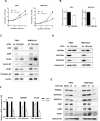
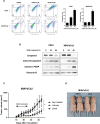
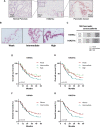
The activity of histone acetyltransferases (HATs) plays a central role in an epigenetic modification in cooperation with HDACs (histone deacetyl transferases). It is likely that malfunction of this enzymatic machinery controlling epigenetic modification is relevant to carcinogenesis and tumor progression. However, in pancreatic cancer, the clinical relevance of HAT activity and histone acetylation has remained unclear. We identified that H3 acetylation was expressed in all pancreatic cancer patients, indicating that H3 acetylation may be essential in pancreatic cancer cells. We also found that the HAT inhibitor C646 augmented anti-tumor effects in vitro by inhibiting cell proliferation and cell cycle progression concomitantly with suppression of acetylated H3K9 and H3K27 expression. C646 or p300 and CBP (CREB-binding protein)-specific siRNA treatment inhibited the transcription of the G2/M cell cycle regulatory proteins cyclin B1 and CDK1 (cyclin-dependent kinase 1). C646 treatment also inhibited tumor growth in vivo in a xenograft mouse model. C646 could be an effective therapeutic agent for pancreatic cancer. The epigenetic status of pancreatic cancers based on their level of histone H3 acetylation may influence patient survival. Epigenetic stratification according to H3K27 acetylation could be useful for predicting disease prognosis as well as the therapeutic efficacy of C646 in pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth by apigenin through induction of G2/M arrest and histone H3 acetylation-mediated p21WAF1/CIP1 expression.Environ Toxicol. 2017 Feb;32(2):434-444. doi: 10.1002/tox.22247. Epub 2016 Feb 12. Environ Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 26872304
-
Histone acetyltransferase p300/CBP inhibitor C646 blocks the survival and invasion pathways of gastric cancer cell lines.Int J Oncol. 2017 Dec;51(6):1860-1868. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4176. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29075795
-
An inhibitor of the acetyltransferases CBP/p300 exerts antineoplastic effects on gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells.Oncol Rep. 2016 Nov;36(5):2763-2770. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5080. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27633918
-
SKLB316, a novel small-molecule inhibitor of cell-cycle progression, induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo.Cancer Lett. 2014 Dec 28;355(2):297-309. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.09.042. Epub 2014 Oct 7. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25301449
-
Histone acetylation and the cell-cycle in cancer.Front Biosci. 2001 Apr 1;6:D610-29. doi: 10.2741/1wang1. Front Biosci. 2001. PMID: 11282573 Review.
Cited by
-
Adipocyte-mediated epigenomic instability in human T-ALL cells is cytotoxic and phenocopied by epigenetic-modifying drugs.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 19;10:909557. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.909557. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36060800 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic Anhydrase 3 is required for cardiac repair post myocardial infarction via Smad7-Smad2/3 signaling pathway.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Feb 25;20(5):1796-1814. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.91396. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38481818 Free PMC article.
-
Multidimensional analyses identify genes of high priority for pancreatic cancer research.JCI Insight. 2025 Jan 7;10(4):e174264. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.174264. JCI Insight. 2025. PMID: 39774001 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic dysregulation of EP300 in cancers in light of cancer epigenome control - targeting of p300-proficient and -deficient cancers.Mol Ther Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;32(4):200871. doi: 10.1016/j.omton.2024.200871. eCollection 2024 Dec 19. Mol Ther Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39351073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type II Interleukin-4 Receptor Activation in Basal Breast Cancer Cells Promotes Tumor Progression via Metabolic and Epigenetic Modulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 24;25(9):4647. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094647. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38731867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguirre AJ, et al. Real-time genomic characterization of advanced pancreatic cancer to enable precision medicine. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:1096–1111. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0275. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

