Supplementation of Lactobacillus early in life alters attention bias to threat in piglets
- PMID: 33980959
- PMCID: PMC8115133
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-89560-2
Supplementation of Lactobacillus early in life alters attention bias to threat in piglets
Abstract
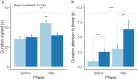
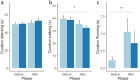
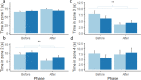
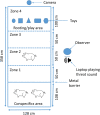
Gut microbes play an important role in regulating brain processes and influence behaviour, cognition and emotional states in humans and rodents. Nevertheless, it is not known how ingestion of beneficial microbes modulates emotional states in piglets and whether it can improve welfare. Here we use an attention bias task to assess the effects of Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC-PTA-6475 and Lactobacillus plantarum L1-6 supplementation early in life on emotional states in 33 piglets compared to 31 placebo supplemented piglets. We hypothesized that Lactobacillus supplementation would reduce vigilance behaviour (head at shoulder height or higher) and attention (head oriented towards the threat) in response to an auditory threat. The results showed that the control group increased vigilance behaviour in response to the threat, but there was no increase in the probiotics group. Despite the increased vigilance, the control group paid less attention to the threat. One explanation may be that control piglets avoided looking in the direction of the threat just because they perceived it as more threatening, but further research is necessary to confirm this. In conclusion, Lactobacillus supplementation may be a suitable tool to reduce anxiety, promote a more appropriate response to a challenge and so improve welfare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

