Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers for Bioactive Delivery
- PMID: 33981670
- PMCID: PMC8107723
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.580118
Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers for Bioactive Delivery
Abstract
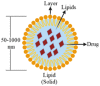
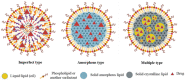
Nanotechnology has made a great impact on the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, food, and cosmetics industries. More than 40% of the approved drugs are lipophilic and have poor solubility. This is the major rate-limiting step that influences the release profile and bioavailability of drugs. Several approaches have been reported to administer lipophilic drugs with improved solubility and bioavailability. Nanotechnology plays a crucial role in the targeted delivery of poorly soluble drugs. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems can be classified as solid lipid nanoparticulate drug delivery systems, emulsion-based nanodrug delivery systems, vesicular drug delivery systems, etc. Nanotechnology presents a new frontier in research and development to conquer the limitations coupled with the conventional drug delivery systems through the formation of specific functionalized particles. This review presents a bird's eye view on various aspects of lipid nanoparticles as carriers of bioactive molecules that is, synthesis, characterization, advantage, disadvantage, toxicity, and application in the medical field. Update on recent development in terms of patents and clinical trials of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) and nanostructure lipid carriers (NLCs) have also been discussed in this article.
Keywords: nanostructure lipid carriers; recent advances; scale up; solid lipid nanoparticles; stability; toxicity.
Copyright © 2021 Dhiman, Awasthi, Sharma, Kharkwal and Kulkarni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ag Seleci D., Seleci M., Walter J. G., Stahl F., Scheper T. (2016). Niosomes as nanoparticular drug carriers: fundamentals and recent applications. J. Nanomater. 2016:7372306. 10.1155/2016/7372306 - DOI
-
- Alarifi1 S., Massadeh S., Al-Agamy M., Al Aamery M., Al Bekairy A. (2020). Enhancement of ciprofloxacin activity by incorporating it in solid lipid nanoparticles. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 19, 909–918. 10.4314/tjpr.v19i5.1 - DOI
-
- Almeida H., Lobão P., Frigerio C., Fonseca J., Silva R., Sousa Lobo J. M., et al. (2015). Preparation, characterization and biocompatibility studies of thermoresponsiveeyedrops based on the combination of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) and the polymer Pluronic F-127 for controlled delivery of ibuprofen. Pharma. Dev. Technol. 22, 336–349. 10.3109/10837450.2015.1125922 - DOI - PubMed
-
- ASTM International E2865-12. (2015). Standard Guide for Measurement of Electrophoretic Mobility and Zeta Potential of Nanosized Biological Materials. ASTM, 1–7.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

