Smallholder farmers' perception of climate change and adoption of climate smart agriculture practices in Masaba South Sub-county, Kisii, Kenya
- PMID: 33981877
- PMCID: PMC8085708
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06789
Smallholder farmers' perception of climate change and adoption of climate smart agriculture practices in Masaba South Sub-county, Kisii, Kenya
Abstract
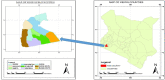
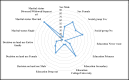
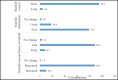
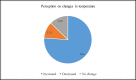
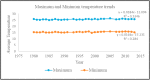
Many countries experience the negative impacts of climate change especially in the decline of agricultural productivity leading to decreased national and household food security. This study assessed smallholder farmers' perception of climate variability and change and their adaptation strategies in Masaba South Sub-County, Kisii County, Kenya. A multi-stage sampling technique was used to collect data from 196 smallholder farmers. Additionally, focused group discussions and key informant interviews were used. The study revealed that most farmers perceived climate changes. 88.3% of the respondents noted a decrease in rainfall, 79.1% reported poor rainfall distribution, 88.3% perceived a late onset of rainfall while 76.6% perceived an increase in temperature. The farmers' perception mirrored the actual climatic data trends for the area obtained from the meteorological department. The major climate-smart agriculture practices adopted by farmers in the area included; diversification of crops, change of planting time and crop rotation/mixed cropping. The adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices significantly correlated with the household size, monthly income, access to credit and farmers' perception of climate change. The study recommends the incorporation and prioritization of climate change in the county and government development agenda as a means of enhancing the uptake of climate-smart agricultural practices.
Keywords: Adaptation; Climate variability and change; Climate-smart agriculture; Perception.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Adamgbe E.M., Ujoh F. Effect of variability in rainfall characteristics on maize yield in Gboko, Nigeria. J. Environ. Protect. 2013;4:881–887.
-
- Adimassu Z., Kessler A. Factors affecting farmers’ coping and adaptation strategies to perceived trends of declining rainfall and crop productivity in the central Rift valley of Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2016;5:1–13.
-
- Alhassan H., Kwaka P.A., Adzawla W. Farmers choice of adaptation strategies to climate change and variability in arid region of Ghana. Rev. Agric. Appl. Econ. (RAAE) 2019;22(1):32–40.
-
- Amir S., Saqib Z., Khan M.I., Ali A., Khan M.A., Bokhari S.A., Zaman ul Haq Determinants of farmers’ adaptation to climate change in rain-fed agriculture of Pakistan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020;13(19)
-
- Amir S., Saqib Z., Khan M.I., Khan M.A., Bokhari S.A., Zaman-Ul-haq M., Majid A. Farmers’ perceptions and adaptation practices to climate change in rain-fed area: a case study from district chakwal, Pakistan. Pakistan J. Agric. Sci. 2020;57(2):465–475.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

