Songwriting intervention for cognitively-impaired children with life-limiting conditions: Study protocol
- PMID: 33981908
- PMCID: PMC8085894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conctc.2021.100765
Songwriting intervention for cognitively-impaired children with life-limiting conditions: Study protocol
Abstract
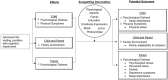
Investigations evaluating the effectiveness of music-based interventions as a complementary approach to symptom management and health promotion for cognitively-impaired children with life-limiting conditions and their families are needed to minimize the physical and psychological burdens on individuals and their caregivers. Songwriting is one music-based strategy for a remote family-centered complementary approach to improve outcomes for cognitively-impaired children with life-limiting conditions, their parents, and families. The overall purpose of this study is to test the feasibility and preliminary efficacy of a songwriting intervention for cognitively-impaired children (ages 5-17 years) who are receiving palliative or complex care and their parents. Specific aims are to: (1) determine the feasibility of songwriting for cognitively-impaired children with life-limiting conditions and their parents, and (2) examine preliminary efficacy of songwriting for child psychological distress and physical symptoms, parent psychological distress, and family environment. The protocol for this 1-group pre-and post-intervention clinical trial (N = 25) is described.
Keywords: Hospice and palliative care nursing; Music therapy; Palliative care; Palliative medicine; Pediatrics; Songwriting.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources