From the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 to neuropathic pain: a potentially novel target
- PMID: 33981930
- PMCID: PMC8108589
- DOI: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000000898
From the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 to neuropathic pain: a potentially novel target
Abstract
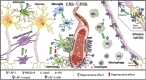
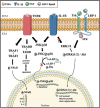
This review describes the roles of the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP-1) in inflammatory pathways, nerve nerve degeneration and -regeneration and in neuropathic pain. Induction of LRP-1 is able to reduce the activation of the proinflammatory NFκB-mediated pathway and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 signaling pathways, in turn decreasing the production of inflammatory mediators. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 activation also decreases reactive astrogliosis and polarizes microglial cells and macrophages from a proinflammatory phenotype (M1) to an anti-inflammatory phenotype (M2), attenuating the neuroinflammatory environment. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 can also modulate the permeability of the blood-brain barrier and the blood-nerve barrier, thus regulating the infiltration of systemic insults and cells into the central and the peripheral nervous system, respectively. Furthermore, LRP-1 is involved in the maturation of oligodendrocytes and in the activation, migration, and repair phenotype of Schwann cells, therefore suggesting a major role in restoring the myelin sheaths upon injury. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 activation can indirectly decrease neurodegeneration and neuropathic pain by attenuation of the inflammatory environment. Moreover, LRP-1 agonists can directly promote neural cell survival and neurite sprouting, decrease cell death, and attenuate pain and neurological disorders by the inhibition of MAPK c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38-pathway and activation of MAPK extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. In addition, activation of LRP-1 resulted in better outcomes for neuropathies such as Alzheimer disease, nerve injury, or diabetic peripheral neuropathy, attenuating neuropathic pain and improving cognitive functions. To summarize, LRP-1 plays an important role in the development of different experimental diseases of the nervous system, and it is emerging as a very interesting therapeutic target.
Keywords: ERK; Inflammation; JNK; LRP-1; NFκB; Neurodegeneration; Neuropathic pain; Neuropathies; Neuroregeneration.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The International Association for the Study of Pain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Postprandial lipoproteins and the molecular regulation of vascular homeostasis.Prog Lipid Res. 2013 Oct;52(4):446-64. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Prog Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23774609 Review.
-
The hemopexin domain of matrix metalloproteinase-9 activates cell signaling and promotes migration of schwann cells by binding to low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein.J Neurosci. 2008 Nov 5;28(45):11571-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3053-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18987193 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin reduces nerve demyelination, neuropathic pain behavior and microglial MAPKs activation through erythropoietin receptors on Schwann cells in a rat model of peripheral neuropathy.Glia. 2018 Nov;66(11):2299-2315. doi: 10.1002/glia.23461. Epub 2018 Nov 11. Glia. 2018. PMID: 30417431
-
Novel Therapeutic Targets in Neuroinflammation and Neuropathic Pain.Inflamm Cell Signal. 2014;1(3):e111. doi: 10.14800/ics.111. Inflamm Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 26052540 Free PMC article.
-
LRP-1: functions, signaling and implications in kidney and other diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Dec 10;15(12):22887-901. doi: 10.3390/ijms151222887. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25514242 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LRP1-Mediated Endocytosis May Be the Main Reason for the Difference in Cytotoxicity of Curcin and Curcin C on U2OS Osteosarcoma Cells.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Nov 8;14(11):771. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110771. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36356021 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization of Hv1/HVCN1 With Antibody Enhances Microglia/Macrophages Myelin Clearance by Promoting Their Migration in the Brain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Oct 22;15:768059. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.768059. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34744634 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Hormones and Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 14;15(7):1013. doi: 10.3390/biom15071013. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of constitutively secreted extracellular chaperones in neuronal cell repair and regeneration.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Apr;18(4):769-772. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.353483. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36204835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Model for Predicting the Effectiveness of Pulsed Radiofrequency on Zoster-Associated Pain.Pain Ther. 2022 Mar;11(1):253-267. doi: 10.1007/s40122-022-00355-3. Epub 2022 Jan 30. Pain Ther. 2022. PMID: 35094299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arthur JS, Ley SC. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2013;13:679–92. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
