SOX9-induced Generation of Functional Astrocytes Supporting Neuronal Maturation in an All-human System
- PMID: 33982246
- PMCID: PMC8553725
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-021-10179-x
SOX9-induced Generation of Functional Astrocytes Supporting Neuronal Maturation in an All-human System
Abstract
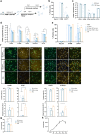
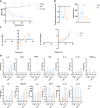
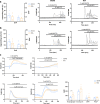
Astrocytes, the main supportive cell type of the brain, show functional impairments upon ageing and in a broad spectrum of neurological disorders. Limited access to human astroglia for pre-clinical studies has been a major bottleneck delaying our understanding of their role in brain health and disease. We demonstrate here that functionally mature human astrocytes can be generated by SOX9 overexpression for 6 days in pluripotent stem cell (PSC)-derived neural progenitor cells. Inducible (i)SOX9-astrocytes display functional properties comparable to primary human astrocytes comprising glutamate uptake, induced calcium responses and cytokine/growth factor secretion. Importantly, electrophysiological properties of iNGN2-neurons co-cultured with iSOX9-astrocytes are indistinguishable from gold-standard murine primary cultures. The high yield, fast timing and the possibility to cryopreserve iSOX9-astrocytes without losing functional properties makes them suitable for scaled-up production for high-throughput analyses. Our findings represent a step forward to an all-human iPSC-derived neural model for drug development in neuroscience and towards the reduction of animal use in biomedical research.
Keywords: All-human co-culture system; Astrocytes; Differentiation protocol; Genome engineering; Pluripotent stem cells.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neonatal mouse cortical but not isogenic human astrocyte feeder layers enhance the functional maturation of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons in culture.Glia. 2018 Apr;66(4):725-748. doi: 10.1002/glia.23278. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Glia. 2018. PMID: 29230877
-
Astrocyte lineage cells are essential for functional neuronal differentiation and synapse maturation in human iPSC-derived neural networks.Glia. 2019 Oct;67(10):1893-1909. doi: 10.1002/glia.23666. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Glia. 2019. PMID: 31246351
-
Role of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Spinal Cord Astrocytes in the Functional Maturation of Motor Neurons in a Multielectrode Array System.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Dec;8(12):1272-1285. doi: 10.1002/sctm.19-0147. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31631575 Free PMC article.
-
[Hypoxia epigenetically bestows astrocytic differentiation potential on human pluripotent cell-derived neural stem/precursor cells].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2019;153(2):54-60. doi: 10.1254/fpj.153.54. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30745514 Review. Japanese.
-
Modeling neurological diseases using iPSC-derived neural cells : iPSC modeling of neurological diseases.Cell Tissue Res. 2018 Jan;371(1):143-151. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2713-x. Epub 2017 Oct 28. Cell Tissue Res. 2018. PMID: 29079884 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elevated α-synuclein levels inhibit mitophagic flux.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Apr 9;10(1):80. doi: 10.1038/s41531-024-00696-0. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 38594264 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Molecular Classification Method for Glioblastoma Based on Tumor Cell Differentiation Trajectories.Stem Cells Int. 2023 Feb 22;2023:2826815. doi: 10.1155/2023/2826815. eCollection 2023. Stem Cells Int. 2023. PMID: 37964983 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 Expression Is Increased in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Is Associated With Disease Progression and APOE4 Genotype: A Computational Approach.Cureus. 2023 Mar 14;15(3):e36129. doi: 10.7759/cureus.36129. eCollection 2023 Mar. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37065298 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient derivation of functional astrocytes from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs).PLoS One. 2024 Dec 4;19(12):e0313514. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0313514. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39630626 Free PMC article.
-
Human iPSC-Derived Astrocytes: A Powerful Tool to Study Primary Astrocyte Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Rare Leukodystrophies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 27;23(1):274. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010274. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008700 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

