Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: normal values of spleen stiffness in healthy children
- PMID: 33983453
- PMCID: PMC8426224
- DOI: 10.1007/s00247-021-05079-8
Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: normal values of spleen stiffness in healthy children
Abstract
Background: Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) imaging is a noninvasive ultrasound elastography technique for evaluating tissue stiffness. The association of liver and spleen stiffness provides additional information in the assessment of portal hypertension. The technique and normal values of spleen stiffness by point shear wave elastography (p-SWE) in pediatrics have not been well documented.
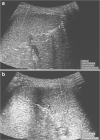
Objective: Our aim is to describe the feasibility and normal ARFI elastography values in the spleen for healthy children and to compare measurements in two different probe positions (the axial and sagittal planes).
Materials and methods: Spleen p-SWE using ARFI values were measured with a 6C1 probe in 102 healthy children (age range: 8 weeks to 17 years) divided into four age groups. An average of nine (standard deviation: two) spleen stiffness measurements were taken during free breathing in each plane (axial and sagittal). The impact of age and measurement plane in the spleen was analyzed using multivariate models.
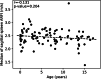
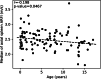
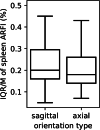
Results: There was no significant difference in spleen stiffness values taken at different ages, with an average of the medians of 2.43±0.31 m/s. There was no significant difference based on probe orientation: sagittal plane (median: 2.46±0.29 m/s) and axial plane (median: 2.43±0.32 m/s) with Student's t-test P=0.18. The mean depth of measurement varied between 2.3 cm and 3.7 cm, according to age.
Conclusion: Normal spleen stiffness values using ARFI imaging in children do not vary with age and correspond to a median of 2.43 m/s. No significant difference was found when using different probe positions.
Keywords: Acoustic radiation force impulse; Children; Normal values; Shear wave elastography; Spleen; Stiffness; Ultrasound.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

