Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Heart Failure
- PMID: 33983836
- PMCID: PMC8136750
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318241
Cardiac Energy Metabolism in Heart Failure
Abstract
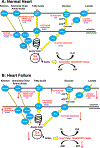
Alterations in cardiac energy metabolism contribute to the severity of heart failure. However, the energy metabolic changes that occur in heart failure are complex and are dependent not only on the severity and type of heart failure present but also on the co-existence of common comorbidities such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. The failing heart faces an energy deficit, primarily because of a decrease in mitochondrial oxidative capacity. This is partly compensated for by an increase in ATP production from glycolysis. The relative contribution of the different fuels for mitochondrial ATP production also changes, including a decrease in glucose and amino acid oxidation, and an increase in ketone oxidation. The oxidation of fatty acids by the heart increases or decreases, depending on the type of heart failure. For instance, in heart failure associated with diabetes and obesity, myocardial fatty acid oxidation increases, while in heart failure associated with hypertension or ischemia, myocardial fatty acid oxidation decreases. Combined, these energy metabolic changes result in the failing heart becoming less efficient (ie, a decrease in cardiac work/O2 consumed). The alterations in both glycolysis and mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in the failing heart are due to both transcriptional changes in key enzymes involved in these metabolic pathways, as well as alterations in NAD redox state (NAD+ and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide levels) and metabolite signaling that contribute to posttranslational epigenetic changes in the control of expression of genes encoding energy metabolic enzymes. Alterations in the fate of glucose, beyond flux through glycolysis or glucose oxidation, also contribute to the pathology of heart failure. Of importance, pharmacological targeting of the energy metabolic pathways has emerged as a novel therapeutic approach to improving cardiac efficiency, decreasing the energy deficit and improving cardiac function in the failing heart.
Keywords: acetylation; diabetic cardiomyopathies; insulin resistance; ketones; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Lopaschuk GD, Ussher JR, Folmes CD, Jaswal JS, Stanley WC. Myocardial fatty acid metabolism in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010;90:207–258 - PubMed
-
- Neubauer S The failing heart — an engine out of fuel. N. Engl. J. Med 2007;356:1140–1151 - PubMed
-
- Kochanek KD, Xu J, Murphy SL, Minino AM, Kung HC. Deaths: Final data for 2009. Natl. Vital Stat. Rep 2011;60:1–116 - PubMed
-
- Mozaffarian D, Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de Ferranti S, Despres JP, Fullerton HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the american heart association. Circ. 2016;133:e38–360 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL142628/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL152354/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R61 HL141783/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133011/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127764/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R33 HL141783/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112413/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL133011/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL129510/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL144937/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- Canadian Institute for Health Research
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

