An electrochemical biosensor for sensitive analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA
- PMID: 33984795
- PMCID: PMC8107000
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113309
An electrochemical biosensor for sensitive analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA
Abstract
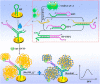
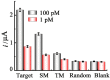
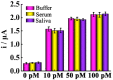
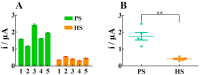
The pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is continuously worsening globally, herein we have proposed an electrochemical biosensor for the sensitive monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. The presence of target RNA firstly triggers the catalytic hairpin assembly circuit and then initiates terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated DNA polymerization. Consequently, a large number of long single-stranded DNA products can be produced, and these negatively charged DNA products will bind a massive of positively charged electroactive molecular of Ru(NH3)63+ due to the electrostatic adsorption. Therefore, significantly amplified electrochemical signals can be generated for sensitive analysis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the range of 0.1-1000 pM with the detection limit as low as 26 fM. Besides the excellent distinguishing ability for SARS-CoV-2 RNA against single-base mismatched RNA, the proposed biosensor can also be successfully applied to complex matrices, as well as clinical patient samples with high stability, which shows great prospects of clinical application.
Keywords: COVID-19; Catalytic hairpin assembly; SARS-CoV-2; TdT-mediated DNA polymerization.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Chen J.Y., Liu Z.J., Wang X.W., Ye C.L., Zheng Y.J., Peng H.P., Zhong G.X., Liu A.L., Chen W., Lin X.H. Anal. Chem. 2019;91:4552–4558. - PubMed
-
- Corman V.M., Landt O., Kaiser M., Molenkamp R., Meijer A., Chu D.K., Bleicker T., Brünink S., Schneider J., Schmidt M.L., Mulders D.G., Haagmans B.L., van der Veer B., van den Brink S., Wijsman L., Goderski G., Romette J.L., Ellis J., Zambon M., Peiris M., Goossens H., Reusken C., Koopmans M.P., Drosten C. Euro Surveill. 2020;25:2000045.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

