Application of 3D bioprinting in the prevention and the therapy for human diseases
- PMID: 33986257
- PMCID: PMC8119699
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00566-8
Application of 3D bioprinting in the prevention and the therapy for human diseases
Abstract
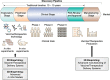
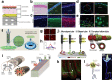
Rapid development of vaccines and therapeutics is necessary to tackle the emergence of new pathogens and infectious diseases. To speed up the drug discovery process, the conventional development pipeline can be retooled by introducing advanced in vitro models as alternatives to conventional infectious disease models and by employing advanced technology for the production of medicine and cell/drug delivery systems. In this regard, layer-by-layer construction with a 3D bioprinting system or other technologies provides a beneficial method for developing highly biomimetic and reliable in vitro models for infectious disease research. In addition, the high flexibility and versatility of 3D bioprinting offer advantages in the effective production of vaccines, therapeutics, and relevant delivery systems. Herein, we discuss the potential of 3D bioprinting technologies for the control of infectious diseases. We also suggest that 3D bioprinting in infectious disease research and drug development could be a significant platform technology for the rapid and automated production of tissue/organ models and medicines in the near future.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020;323:1239–1242. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mullard A. Hints of hope with remdesivir. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2020;19:373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

