Protein-based antigen presentation platforms for nanoparticle vaccines
- PMID: 33986287
- PMCID: PMC8119681
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-021-00330-7
Protein-based antigen presentation platforms for nanoparticle vaccines
Abstract
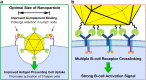
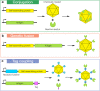
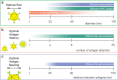
Modern vaccine design has sought a minimalization approach, moving to the isolation of antigens from pathogens that invoke a strong neutralizing immune response. This approach has created safer vaccines but may limit vaccine efficacy due to poor immunogenicity. To combat global diseases such as COVID-19, malaria, and AIDS there is a clear urgency for more effective next-generation vaccines. One approach to improve the immunogenicity of vaccines is the use of nanoparticle platforms that present a repetitive array of antigen on its surface. This technology has been shown to improve antigen presenting cell uptake, lymph node trafficking, and B-cell activation through increased avidity and particle size. With a focus on design, we summarize natural platforms, methods of antigen attachment, and advancements in generating self-assembly that have led to new engineered platforms. We further examine critical parameters that will direct the usage and development of more effective platforms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- FDA. Drug Products, Including Biological Products, that Contain Nanomaterials—Guidance for Industry, https://www.fda.gov/media/109910/download (FDA, 2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Song C, et al. Recent advances in particulate adjuvants for cancer vaccination. Adv. Therapeutics. 2020;3:1900115. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201900115. - DOI
-
- Shin H, et al. Recent advances in RNA therapeutics and RNA delivery systems based on nanoparticles. Adv. Therapeutics. 2018;1:1800065. doi: 10.1002/adtp.201800065. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

