Electroacupuncture Attenuates Cognitive Impairment in Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion via miR-137/NOX4 Axis
- PMID: 33986822
- PMCID: PMC8079190
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8842022
Electroacupuncture Attenuates Cognitive Impairment in Rat Model of Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion via miR-137/NOX4 Axis
Abstract
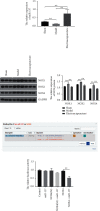
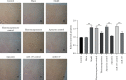
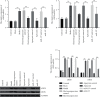
Electroacupuncture has shown protective effects on cognitive decline. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not clear. The present study was conducted to determine whether the cognitive function was ameliorated in cerebral hypoperfusion rats following electroacupuncture and to investigate the role of miR-137/NOX4 axis. In this study, chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) model was established by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion. Electroacupuncture treatment attenuated brain injury in CCH model group via regulating miR-137/NOX4 axis. Furthermore, the data of neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress were observed. Our findings indicated that (1) neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress in CCH rats were significantly increased compared with control group; (2) the animal cognitive performance was evaluated using the Morris water maze (MWM). The results showed that electroacupuncture therapy ameliorated spatial learning and memory impairment in cerebral hypoperfusion rats; and (3) electroacupuncture therapy reduces neuronal apoptosis and oxidative stress by activating miR-137/NOX4 axis. These results suggest that electroacupuncture therapy for CCH may be mediated by miR-137/NOX4 axis. Electroacupuncture therapy may act as a potential therapeutic approach for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.
Copyright © 2021 Xiaochen Bi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in the publication of this manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Cechetti F., Worm P. V., Pereira L. O., Siqueira I. R., Netto A. C. The modified 2VO ischemia protocol causes cognitive impairment similar to that induced by the standard method, but with a better survival rate. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 2010;43(12):1178–1183. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2010007500124. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

