SS-31 Protects Liver from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Modulating Macrophage Polarization
- PMID: 33986918
- PMCID: PMC8057883
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6662156
SS-31 Protects Liver from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Modulating Macrophage Polarization
Abstract
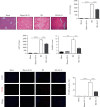
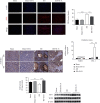
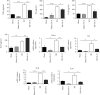
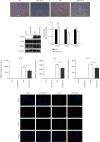
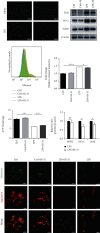
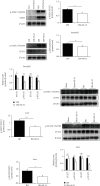
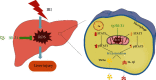
Ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) is a common complication in liver surgeries. It is a focus to discover effective treatments to reduce ischemia-reperfusion injury. Previous studies show that oxidative stress and inflammation response contribute to the liver damage during IRI. SS-31 is an innovated mitochondrial-targeted antioxidant peptide shown to scavenge reactive oxygen species and decrease oxidative stress, but the protective effects of SS-31 against hepatic IRI are not well understood. The aim of our study is to investigate whether SS-31 could protect the liver from damages induced by IRI and understand the protective mechanism. The results showed that SS-31 treatment can significantly attenuate liver injury during IRI, proved by HE staining, serum ALT/AST, and TUNEL staining which can assess the degree of liver damage. Meanwhile, we find that oxidative stress and inflammation were significantly suppressed after SS-31 administration. Furthermore, the mechanism revealed that SS-31 can directly decrease ROS production and regulate STAT1/STAT3 signaling in macrophages, thus inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization. The proinflammation cytokines are then significantly reduced, which suppress inflammation response in the liver. Taken together, our study discovered that SS-31 can regulate macrophage polarization through ROS scavenging and STAT1/STAT3 signaling to ameliorate liver injury; the protective effects against hepatic IRI suggest that SS-31 may be an appropriate treatment for liver IRI in the clinic.
Copyright © 2021 Longcheng Shang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Liraglutide Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Modulating Macrophage Polarization.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 5;13:869050. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.869050. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35450076 Free PMC article.
-
Sunitinib alleviates hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT pathway and promoting the M2 polarization of macrophages.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024 Oct;46(5):672-684. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2024.2390455. Epub 2024 Aug 18. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2024. PMID: 39155607
-
NAMPT inhibition reduces macrophage inflammation through the NAD+/PARP1 pathway to attenuate liver ischemia-reperfusion injury.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 Jan 5;369:110294. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110294. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 36460127
-
Macrophage Polarization and Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(5):1104-1113. doi: 10.7150/ijms.52691. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33526969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotheranostics for the Management of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Small. 2021 Jun;17(23):e2007727. doi: 10.1002/smll.202007727. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Small. 2021. PMID: 33852769 Review.
Cited by
-
XJB-5-131 Is a Mild Uncoupler of Oxidative Phosphorylation.J Huntingtons Dis. 2022;11(2):141-151. doi: 10.3233/JHD-220539. J Huntingtons Dis. 2022. PMID: 35404288 Free PMC article.
-
New therapeutic concepts against ischemia-reperfusion injury in organ transplantation.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023 Jul-Dec;19(10):1205-1224. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2023.2240516. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37489289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elamipretide(SS-31) Attenuates Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Nrf2-Dependent NLRP3 Inflammasome in Macrophages.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;12(12):2022. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122022. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136142 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA260 siRNA Accelerates M2 Macrophage Polarization and Alleviates Oxidative Stress via Inhibiting IL28RA Gene Alternative Splicing.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 23;2022:4942519. doi: 10.1155/2022/4942519. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Dec 29;2023:9757834. doi: 10.1155/2023/9757834. PMID: 36193089 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A narrative review on inflammaging and late-onset hypogonadism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 17;15:1291389. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1291389. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38298378 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

