Identification of a five-gene signature in association with overall survival for hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 33986994
- PMCID: PMC8088210
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.11273
Identification of a five-gene signature in association with overall survival for hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is considered to be a malignant tumor with a high incidence and a high mortality. Accurate prognostic models are urgently needed. The present study was aimed at screening the critical genes for prognosis of HCC.
Methods: The GSE25097, GSE14520, GSE36376 and GSE76427 datasets were obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). We used GEO2R to screen differentially expressed genes (DEGs). A protein-protein interaction network of the DEGs was constructed by Cytoscape in order to find hub genes by module analysis. The Metascape was performed to discover biological functions and pathway enrichment of DEGs. MCODE components were calculated to construct a module complex of DEGs. Then, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was used for gene enrichment analysis. ONCOMINE was employed to assess the mRNA expression levels of key genes in HCC, and the survival analysis was conducted using the array from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) of HCC. Then, the LASSO Cox regression model was performed to establish and identify the prognostic gene signature. We validated the prognostic value of the gene signature in the TCGA cohort.
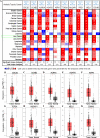
Results: We screened out 10 hub genes which were all up-regulated in HCC tissue. They mainly enrich in mitotic cell cycle process. The GSEA results showed that these data sets had good enrichment score and significance in the cell cycle pathway. Each candidate gene may be an indicator of prognostic factors in the development of HCC. However, hub genes expression was weekly associated with overall survival in HCC patients. LASSO Cox regression analysis validated a five-gene signature (including CDC20, CCNB2, NCAPG, ASPM and NUSAP1). These results suggest that five-gene signature model may provide clues for clinical prognostic biomarker of HCC.
Keywords: Differentially expressed genes; Functional enrichment analysis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognostic analysis.
©2021 Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball C, Blake J, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry J, Davis A, Dolinski K, Dwight S, Eppig J, Harris M, Hill D, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese J, Richardson J, Ringwald M, Rubin G, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nature Genetics. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

