The REALISE score: a new statistically validated scoring system to assess the severity of anal fissures
- PMID: 33987779
- PMCID: PMC8289784
- DOI: 10.1007/s10151-021-02459-y
The REALISE score: a new statistically validated scoring system to assess the severity of anal fissures
Abstract
Background: Anal fissure (AF) is a common, painful disease that strongly affects patients' quality of life, however, no scoring system to assess the severity of AF is available in the literature. The aim of this study was to set up and validate a reliable scoring system to quantify the severity of AF, to be used in prospective trials comparing the efficacy and the outcomes of surgical or medical treatments.
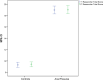
Methods: The study was conducted on patients with acute or chronic AF and a control group in a tertiary centre for coloproctology in June 2020-September 2020. Two researchers independently carried out a structured interviewer-led questionnaire at two different time points (T1/T2). The questionnaire consisted of five items selected according to the most commonly reported symptoms for AF: the item pain, was scored from 0 to 10 using a visual analogue scale, and quality of life, duration of pain, use of painkillers, and bleeding were scored from 1 to 5 using Likert-scale questions. The scoRing systEm for AnaL fIsSurE (REALISE) score was the sum of the points. Patients with AF and a control group of patients with haemorrhoids, anal fistula, or obstructed defecation syndrome entered the study. Main outcome measures were reliability, inter-/intraobserver agreement, and repeatability.
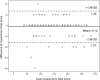
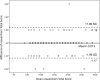
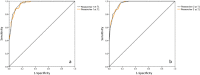
Results: One hundred and fifty well-matched patients (75 with AF and 75 controls) were enrolled. A significant difference was found between the mean REALISE score for patients with AF and controls (p < 0.001). The two REALISE scores were highly correlated (r = 0.99). The coefficient of repeatability was 1.45 in T1 and 1.18 in T2.
Conclusions: The REALISE score may have an important role in the assessment and management of AF, in grading the severity of AF and comparing results of different treatments.
Keywords: Anal fissure; Inter-/intraobserver agreement; Reliability; Repeatability; Scoring system.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

