Functional connexin35 increased in the myopic chicken retina
- PMID: 33988110
- PMCID: PMC8167454
- DOI: 10.1017/S0952523821000079
Functional connexin35 increased in the myopic chicken retina
Erratum in
-
Functional connexin35 increased in the myopic chicken retina-CORRIGENDUM.Vis Neurosci. 2021 Jul 23;38:E009. doi: 10.1017/S0952523821000109. Vis Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34294173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
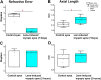
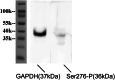
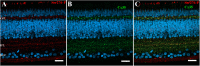
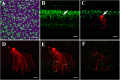
Our previous research showed that increased phosphorylation of connexin (Cx)36 indicated extended coupling of AII amacrine cells (ACs) in the rod-dominant mouse myopic retina. This research will determine whether phosphorylation at serine 276 of Cx35-containing gap junctions increased in the myopic chicken, whose retina is cone-dominant. Refractive errors and ocular biometric dimensions of 7-days-old chickens were determined following 12 h and 7 days induction of myopia by a -10D lens. The expression pattern and size of Cx35-positive plaques were examined in the early (12 h) and compensated stages (7 days) of lens-induced myopia (LIM). At the same time, phosphorylation at serine 276 (functional assay) of Cx35 in strata 5 (S5) of the inner plexiform layer was investigated. The axial length of the 7 days LIM eyes was significantly longer than that of non-LIM controls (P < 0.05). Anti-phospho-Ser276 (Ser276-P)-labeled plaques were significantly increased in LIM retinas at both 12 h and 7 days. The density of Ser276-P of Cx35 was observed to increase after 12 h LIM. In the meanwhile, the areas of existing Cx35 plaques did not change. As there was more phosphorylation of connexin35 at Ser276 at both the early and late stages (12 h) and 7 days of LIM chicken retinal activity, the coupling with ACs could be increased in myopia development of the cone-dominated chicken retina.
Keywords: amacrine cell; gap junction; myopia; retina.
Figures
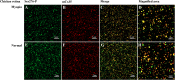
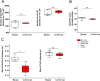

Similar articles
-
Connexin35/36 gap junction proteins are expressed in photoreceptors of the tiger salamander retina.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Feb 23;470(1):1-12. doi: 10.1002/cne.10967. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 14755521
-
Increased Connexin36 Phosphorylation in AII Amacrine Cell Coupling of the Mouse Myopic Retina.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Jun 1;14:124. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00124. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32547367 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin 35/36 is phosphorylated at regulatory sites in the retina.Vis Neurosci. 2007 May-Jun;24(3):363-75. doi: 10.1017/S095252380707037X. Epub 2007 Jul 20. Vis Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17640446 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal ganglion cells encode differently in the myopic mouse retina?Exp Eye Res. 2023 Sep;234:109616. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2023.109616. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Exp Eye Res. 2023. PMID: 37580002
-
Electrical synapses between AII amacrine cells in the retina: Function and modulation.Brain Res. 2012 Dec 3;1487:160-72. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.05.060. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22776293 Review.
Cited by
-
Functional connexin35 increased in the myopic chicken retina-CORRIGENDUM.Vis Neurosci. 2021 Jul 23;38:E009. doi: 10.1017/S0952523821000109. Vis Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34294173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Role of Retinal Dysfunction in Myopia Development.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jul;43(5):1905-1930. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01309-1. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36427109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of computer-generated patterns with different temporal and spatial frequencies on choroidal thickness, retinal dopamine and candidate genes in chickens wearing lenses.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 10;11:1469275. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1469275. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39720655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bloomfield, S.A. & Volgyi, B. (2004). Function and plasticity of homologous coupling between AII amacrine cells. Vision Research 44, 3297–3306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

