Is 2020 the golden year of Otolaryngology research? The impact of COVID-19 on the Italian academic production
- PMID: 33988134
- PMCID: PMC8182618
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v92i2.11557
Is 2020 the golden year of Otolaryngology research? The impact of COVID-19 on the Italian academic production
Abstract
Background and aim: The aim of this research was to review the articles published by the Otolaryngology (ORL) departments of the Italian University Hospitals in 2019 and in 2020 in order to analyze the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the academic production.
Methods: PubMed and Scopus were searched for the articles published by the ORL departments of the Italian Universities in 2019 and in 2020. The main eligibility criteria were English-language articles, while there were no exclusion criteria related to topic. The articles were classified into seven domains corresponding to the main ORL subspecialties.
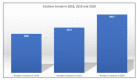
Results: There was an overall increase in the number of articles by the 42.2% in 2020. Publications pertaining Rhinology and Laryngology increased more significantly in 2020, respectively by the 50.5% and 72.2%. Additionally, there was an increase in the number of articles concerning topics of general interest, by the 95.2% in 2020. Also, the citation trends of the articles published by the Italian University Hospitals increased remarkably in 2020.
Conclusions: These results evidenced an overall increase in the number of ORL articles. Although 2020 is going to be remembered as a year to forget, it should be acknowledged for being the "golden year of research".
Conflict of interest statement
Each author declares that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g., consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Figures
References
-
- Vukkadala N, Qian ZJ, Holsinger FC, Patel ZM, Rosenthal E. COVID-19 and the otolaryngologist - preliminary evidence-based review. Laryngoscope. Published online 2020. doi: 10.1002/lary.28672. - PubMed
-
- Huart C, Philpott C, Konstantinidis I, et al. Comparison of COVID-19 and common cold chemosensory dysfunction. Rhinology. Published online 2020. doi: 10.4193/Rhin20.251. - PubMed
-
- Niklassen AS, Draf J, Huart C, et al. COVID-19: Recovery from Chemosensory Dysfunction. A Multicentre study on Smell and Taste. Laryngoscope. Published online January 15, 2021:lary.29383. doi: 10.1002/lary.29383. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical