Is there a role for neuregulin 4 in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?
- PMID: 33989346
- PMCID: PMC8121306
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251822
Is there a role for neuregulin 4 in human nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?
Abstract
Background: Neuregulin 4 (Nrg4), a novel adipokine enriched in brown adipose tissue has been observed to negatively regulate de novo hepatic lipogenesis and limit nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) progression to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in rodents. However, the role of Nrg4 in human NAFLD remains unclear to date. We analysed Nrg4 plasma levels and its association with liver disease severity together with the transcriptional profile of the Nrg4 pathway in liver and visceral adipose tissue (VAT) of NAFLD patients.
Methods: Plasma Nrg4 levels were measured in 65 NAFLD patients and 43 healthy controls (HC). Hepatic steatosis and fibrosis were diagnosed and quantified with chemical shift MRI and transient elastography respectively. Furthermore, blood lipid levels, HOMA-IR and systemic pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IFN-γ) were analysed. Microarray analyses to assess differences in the Nrg4 and its receptor family ErbB pathway in liver and VAT from an independent patient group with biopsy proven NAFL (simple steatosis) (n = 4), NASH (n = 5) and normal liver (n = 6) were performed.
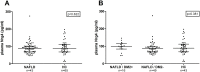
Results: Plasma Nrg4 levels were not significantly different between NAFLD patients and HC (p = 0.622). Furthermore, plasma Nrg4 levels did not correlate with the hepatic fat fraction (r = -0.028, p = 0.829) and were not significantly different between NAFLD patients with or without hepatic fibrosis (p = 0.087). Finally, the expression profile of 82 genes related to the Nrg4-ErbB pathway in liver and VAT was not significantly different between NAFL, NASH or obese controls.
Conclusion: Our study does not support a role for Nrg4 in the pathophysiology of human NAFLD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nrg4 promotes fuel oxidation and a healthy adipokine profile to ameliorate diet-induced metabolic disorders.Mol Metab. 2017 Jun 21;6(8):863-872. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.03.016. eCollection 2017 Aug. Mol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28752050 Free PMC article.
-
A case-control study: Association between serum neuregulin 4 level and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Metabolism. 2015 Dec;64(12):1667-73. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2015.08.013. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Metabolism. 2015. PMID: 26476959
-
The Putative Antilipogenic Role of NRG4 and ERBB4: First Expression Study on Human Liver Samples.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 Dec 11;29(12):414. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2912414. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 39735994
-
Metabolic drivers of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Mol Metab. 2021 Aug;50:101143. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101143. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33346069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Liver Biopsy in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: When to Biopsy and in Whom.Clin Liver Dis. 2018 Feb;22(1):109-119. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2017.08.006. Clin Liver Dis. 2018. PMID: 29128050 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuregulin-4 attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR signalling pathway.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Oct 11;21(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01643-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 36221104 Free PMC article.
-
Novel secreted regulators of glucose and lipid metabolism in the development of metabolic diseases.Diabetologia. 2024 Dec;67(12):2626-2636. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06253-x. Epub 2024 Aug 24. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 39180580 Review.
-
The impact of serum neuregulin 4 (NRG-4) levels on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 9;25(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04097-2. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40634833 Free PMC article.
-
Neuregulin 4 as a novel adipokine in energy metabolism.Front Physiol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1106380. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1106380. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36703934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low circulating levels of neuregulin 4 as a potential biomarker associated with the severity and prognosis of obesity-related metabolic diseases: a systematic review.Adipocyte. 2024 Dec;13(1):2390833. doi: 10.1080/21623945.2024.2390833. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Adipocyte. 2024. PMID: 39162358 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

