Effect of the Mendelsohn maneuver and swallowing training in patients with senile vascular dementia complicated with dysphagia
- PMID: 33990151
- PMCID: PMC8127777
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605211013198
Effect of the Mendelsohn maneuver and swallowing training in patients with senile vascular dementia complicated with dysphagia
Retraction in
-
Retraction Notice.J Int Med Res. 2024 Jan;52(1):3000605241228165. doi: 10.1177/03000605241228165. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38217421 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: We investigated the effect of the Mendelsohn maneuver and swallowing training in patients with senile vascular dementia complicated with dysphagia.
Methods: We randomly classified 214 patients with senile vascular dementia and swallowing dysfunction into a control group (CG, n = 106) and observation group (OG, n = 108). Both groups underwent health education, psychological intervention, and training of the oral muscle group. The OG additionally underwent the Mendelsohn maneuver and swallowing training. The Hasegawa Dementia Scale (HDS), China Stroke Scale (CSS), and Neurobehavioral Cognitive Status Examination (NCSE) were used to evaluate dementia, neurological impairment, and cognitive dysfunction, respectively.
Results: The OG had a higher rate of effective therapy than the CG. After intervention, the OG showed better swallowing function than the CG. At 15 days and 1 month after intervention, the OG had higher video fluoroscopic swallowing exam scores than the CG. The OG had lower serum interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels than the CG. After intervention, the OG had higher HDS and NCSE scores and lower CSS scores than the CG.
Conclusions: The Mendelsohn maneuver and swallowing training can improve swallowing function in patients with senile vascular dementia complicated with dysphagia and help to ameliorate the inflammatory response.
Keywords: Mendelsohn maneuver; Vascular dementia; dysphagia; inflammatory factor; swallowing function; swallowing training.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
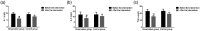
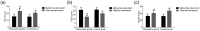
References
-
- Kawano H, Mori T, Kuroki A, et al. Candy eating behaviour to improve swallowing function in dementia subjects. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2018; 75: 181–184. - PubMed
-
- Barsotti S, Puccini G, Tripoli A, et al. Assessment of swallowing function with oro-pharyngeal-esophageal scintigraphy in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2019; 31: e13599. - PubMed
-
- Tedesco A, Lavermicocca V, Notarnicola M, et al . [Telemonitoring of swallowing function: technologies in speech therapy practice.] Recenti Prog Med 2018; 109: 146–148. - PubMed
-
- Imai Y, Hasegawa K. The Revised Hasegawa Dementia Scale (HDS-R) – evaluation of its usefulness as a screening test for dementia. J Hong Kong Coll Psychiatr 1994; 4: 20–24.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

