Demarcation of arteriopulmonary segments: a novel and effective method for the identification of pulmonary segments
- PMID: 33990153
- PMCID: PMC8127771
- DOI: 10.1177/03000605211014383
Demarcation of arteriopulmonary segments: a novel and effective method for the identification of pulmonary segments
Abstract
Objective: Each pulmonary segment is an anatomical and functional unit. However, it is fundamentally difficult to precisely distinguish every pulmonary segment using the conventional pulmonary intersegmental planes from computed tomography images. Building arteriopulmonary segments is likely to be an effective way to identify pulmonary segments.
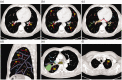
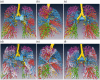
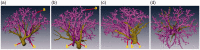
Methods: The thoracic computed tomography images of 40 patients were collected. The anatomic structures of interest were extracted in the transverse, sagittal, and coronal planes using the semi-automated segmentation tools provided by Amira software. The intrapulmonary vessels were subsequently segmented and reconstructed. The distributions of the pulmonary arteries, veins, and bronchi were observed. In patients with pulmonary masses, the mass was also reconstructed.
Results: The three-dimensional reconstructed images showed the branches of the pulmonary artery ramified up to their eighth order covering the entire lung as well as evident intersegmental gaps without pulmonary arteries. The segmental artery was closely accompanied by the segmental bronchi in 486 pulmonary segments (90% of total number of segments). The size and spatial location of the pulmonary mass within a pulmonary segment were also clearly visible.
Conclusions: Demarcation of arteriopulmonary segments can be used to precisely distinguish every pulmonary segment and provide its detailed anatomical structure before pulmonary segmentectomy.
Keywords: Lung; arteriopulmonary segment; computed tomography; pulmonary artery; pulmonary mass; segmentectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Trans-Inferior-Pulmonary-Ligament Single-Direction Thoracoscopic RS9 Segmentectomy: Application of Stem-Branch Method for Tracking Anatomy.Ann Surg Oncol. 2020 Aug;27(8):3092-3093. doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-08309-9. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32152779
-
Determination of lung segments in computed tomography images using the Euclidean distance to the pulmonary artery.Med Phys. 2013 Sep;40(9):091912. doi: 10.1118/1.4818017. Med Phys. 2013. PMID: 24007163
-
Thoracoscopic anatomic pulmonary segmentectomy: a 3-dimensional guided imaging system for lung operations.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016 Aug;23(2):183-9. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivw085. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27099268
-
[The Main Technical Points of Thoracoscopic Anatomical Lung Segment Resection].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016 Jun 20;19(6):377-81. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2016.06.16. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27335301 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Lung segments from anatomy to surgery.Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2024;83(1):20-34. doi: 10.5603/FM.a2023.0011. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Folia Morphol (Warsz). 2024. PMID: 36811139 Review.
Cited by
-
The Importance of Topographical Recognition of Pulmonary Arteries in Diagnostics and Treatment of CTEPH, Based on an Analysis of a Dissected Case Model-A Pilot Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 3;14(15):1684. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14151684. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39125560 Free PMC article.
-
An Automated Broncho-Arterial (BA) Pair Segmentation Process and Assessment of BA Ratios in Children with Bronchiectasis Using Lung HRCT Scans: A Pilot Study.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 30;11(7):1874. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071874. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Overholt RH, Gaensler EA, Bougas JA. Single or double segments of the lung occupying a hemithorax; clinical and physiologic evaluation. N Engl J Med 1959; 261: 10–18. - PubMed
-
- Tatsumura T, Sato H, Mori A, et al.. A new surgical approach to apical segment lung diseases, including carcinomas and inflammatory diseases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1994; 107: 32–36. - PubMed
-
- Zhang P, Jiang G, Ding J, et al.. Surgical treatment of bronchiectasis: a retrospective analysis of 790 patients. Ann Thorac Surg 2010; 90: 246–250. - PubMed
-
- Kilic A, Schuchert MJ, Pettiford BL, et al.. Anatomic segmentectomy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer in the elderly. Ann Thorac Surg 2009; 87: 1662–1668. - PubMed
-
- Schuchert MJ, Pettiford BL, Keeley S, et al.. Anatomic segmentectomy in the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 2007; 84: 926–932. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

