Tumor Immunity and Immunotherapy for HPV-Related Cancers
- PMID: 33990345
- PMCID: PMC8338882
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1760
Tumor Immunity and Immunotherapy for HPV-Related Cancers
Abstract
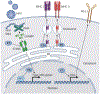
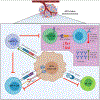
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection drives tumorigenesis in the majority of cervical, oropharyngeal, anal, and vulvar cancers. Genetic and epidemiologic evidence has highlighted the role of immunosuppression in the oncogenesis of HPV-related malignancies. Here we review how HPV modulates the immune microenvironment and subsequent therapeutic implications. We describe the landscape of immunotherapies for these cancers with a focus on findings from early-phase studies exploring antigen-specific treatments, and discuss future directions. Although responses across these studies have been modest to date, a deeper understanding of HPV-related tumor biology and immunology may prove instrumental for the development of more efficacious immunotherapeutic approaches. SIGNIFICANCE: HPV modulates the microenvironment to create a protumorigenic state of immune suppression and evasion. Our understanding of these mechanisms has led to the development of immunomodulatory treatments that have shown early clinical promise in patients with HPV-related malignancies. This review summarizes our current understanding of the interactions of HPV and its microenvironment and provides insight into the progress and challenges of developing immunotherapies for HPV-related malignancies.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interests:
No relevant conflicts of interest to the present publication. Authors receive research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Repare therapeutics as well as honoraria from Illumina and repare therapeutics
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

