Off-label postpartum use of domperidone in Canada: a multidatabase cohort study
- PMID: 33990364
- PMCID: PMC8157989
- DOI: 10.9778/cmajo.20200084
Off-label postpartum use of domperidone in Canada: a multidatabase cohort study
Abstract
Background: Trends in off-label postpartum use of domperidone and the impact of safety advisories on its use remain unknown. Our objectives were to describe postpartum use of domperidone in Canada, to evaluate the impact of Health Canada advisories on prescribing patterns, and to describe the association between domperidone use and a composite end point of sudden cardiac death or ventricular tachycardia (VT) among postpartum patients.
Methods: We conducted a multidatabase cohort study involving pregnant patients with live births between 2004 and 2017 using administrative health databases from 5 Canadian provinces (British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba and Ontario). We excluded patients with less than 1 year of prepregnancy database history and with approved indications for domperidone. We assessed domperidone use in the 6 months postpartum and the impact of the 2012 and 2015 Health Canada advisories on prescribing via interrupted time series analysis. We estimated crude rates of VT and sudden cardiac death.
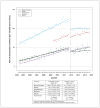
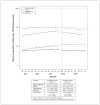
Results: We included 1 190 987 live births. Mean maternal age was 28.6 (standard error 0.6) years. Domperidone use increased over time, from 7% in 2003-2005 to 12% in 2009-2011, when it plateaued. The 2012 advisory was followed by a drop in use and a reduction in slope, and the 2015 advisory had a more modest impact. Crude analysis suggests that domperidone may be associated with increased VT or sudden cardiac death (0.74 v. 0.37 per 10 000 person-years; difference per 10 000 person-years: 0.37, 95% confidence interval -0.67 to 1.41).
Interpretation: Postpartum domperidone use increased between 2004 and 2017, with prescribing attenuated after Health Canada advisories and a very low absolute rate of VT or sudden cardiac death. These findings suggest that Health Canada advisories affected prescribing; any potential increase in VT or sudden cardiac death with use of domperidone is small and could not be confirmed in this large study STUDY REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov, no. NCT04024865.
© 2021 CMA Joule Inc. or its licensors.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Barone JA. Domperidone: a peripherally acting dopamine2-receptor antagonist. Ann Pharmacother. 1999;33:429–40. - PubMed
-
- Campbell-Yeo ML, Allen AC, Joseph KS, et al. Effect of domperidone on the composition of preterm human breast milk. Pediatrics. 2010;125:e107–14. - PubMed
-
- Johannes CB, Varas-Lorenzo C, McQuay LJ, et al. Risk of serious ventricular arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death in a cohort of users of domperidone: a nested case–control study. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2010;19:881–8. - PubMed
-
- Paul C, Zenut M, Dorut A, et al. Use of domperidone as a galactagogue drug: a systematic review of the benefit-risk ratio. J Hum Lact. 2015;31:57–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
